Navigation Menu
This page explains how to set up the Navigation Menu component, enabling you to incorporate drop-down menus to your KX Dashboards.
A navigation menu can connect users to a variety of resources, including other KX Dashboards, external websites, support pages, help resources, user guides, and more.
The following screenshot shows an example menu with links to other KX Dashboards. Configuration of this example is described in the sections below.

Tip
Two levels of menu are supported.
Set up a Navigation Menu
This section outlines the configuration steps. A detailed example is provided in the next section.
-
Click and drag the component into the workspace.

-
Define the following properties:
Property
Description
Name
Enter a name for the component.
Data Source
Configure the data source, which defines the menu structure.
Font Size
Select a font size for the menu items.
Node
Configure the Nodes to map each of the menu elements to the columns in your data source. This is only required if your column names differ from the default columns; Node, Parent, URL, and ID.
Actions
You can configure Actions, a common property set, to manage view states, run queries, or open URLs here.
Style/Format/Margins
Configure the Style, Margins and Format for the menu.
Data source
The Data Source defines the menu structure for the component. For static data, such as navigation menu generation, we recommend using JavaScript in the Virtual tab. This approach is faster and operates independently of the backend process.
-
In the component, Click to populate Data Source or click Data Source in the Basics properties to open the Data dialog. Click New to proceed.
The data source, for the Navigation Menu, requires 4 columns which are described in the following table.
Column Name
Description
Node
This is the name of an individual menu item. It can be a top level or drop-down menu item. Each node can be associated with a URL. Each node has a parent (node) defined. If the node is a top-level item in the menu, enter a blank value as its parent. See the example below.
Parent
A parent is a node that has one or more child nodes. In a hierarchical navigation menu, a parent node can be expanded to reveal its child nodes. For instance, the Product Demos parent node, in the example at the top of this page, has the child nodes Demo Health and Demo Sensors.
URL
This is the URL or UUIDs linked to each node/menu option. The UUID of a Dashboard is the part after
edit/in the Dashboard URL. For example, in the URL https://ui-dash.kx.com/dash-main/edit/#f856763f-d4c6-8c6d-6c62-991b299a1a16, the UUID is #f856763f-d4c6-8c6d-6c62-991b299a1a16.When using this component in kdb Insights Enterprise Views, prepend
viewto the UUID. For example,view#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162. This is not required if you are using absolute URLs such as https://code.kx.com.If you want to add a link to the shared view of the View, prepend
view/shareto the UUID. For example,view/share#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162.This is not required if you are using absolute URLs such as https://code.kx.com. You can avoid manually adding
viewandview/shareby using the following code before thecallbackfunction in the JavaScript used to create your menu in the Virtual tab.JavaScript
Copy_.each(results.rows, r => {
if (r.url.indexOf("#") === 0) {
r.url = ($("kx-report-editor").length ? "view" : $("kx-report-viewer").length ? "view/share" : "") + r.url;
}
});This is shown in the views example below.
ID
The ID is a unique identifier assigned to each node/menu item. It helps in distinguishing between different nodes, especially when manipulating the menu programmatically.
You can use different column names in the data source definition, but you must map them to the correct elements using the Node properties.
-
Once you have configured the data source, click Apply and Select Item.
-
Next, you need to map the columns defined in your data source to the Nodes.
Examples
The following sections provides examples of setting up the Navigation Menu in:
KX Dashboards example
The following Javascript code creates the example shown in the KX Dashboards screenshot at the top of this page.
JavaScript
function (source, callback) {
const results = {};
// source is an object representing a data source, with the following properties:
// columns: an array of column names, for example,
results.columns = [
"node",
"parent",
"url",
"id"
];
// meta: an object mapping column names to their kdb types
results.meta = {
"node": 0,
"parent": 0,
"url": 0,
"id": 7
};
// rows: an array of row objects, each one maps columns to values
results.rows = [
{"node":"Visualizations Demos","parent":"","url":"#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162","id":1001},
{"node":"Products Demos","parent":"","url":"#b206840b-2e64-4209-bacd-166c883928f","id":1002},
{"node":"Component Demos","parent":"","url":"#80c52499-cd0a-a1ca-46bb-178be3aaeed","id":1003},
{"node":"Demo Visualize","parent":"Visualizations Demos","url":"#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162","id":1004},
{"node":"Demo Health","parent":"Products Demos","url":"#b206840b-2e64-4209-bacd-166c883928f","id":1005},
{"node":"Demo Sensors","parent":"Products Demos","url":"#c02f1251-9300-2c35-9efe-85a0b87665f4","id":1006},
{"node":"Data","parent":"Component Demos","url":"#80c52499-cd0a-a1ca-46bb-178be3aaeed","id":1007},
{"node":"Graph","parent":"Component Demos","url":"#b58fe5e3-d02f-3130-2e53-5bddc0bbac3d","id":1008}
];
// you can perform operations on the source, generate values or fetch remote data using javascript
// when you are done pass an object in the same format as source to the callback function to return your data
callback(results);
}This example contains the following elements:
|
Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Defines an anonymous function that takes two parameters: source and callback. |
|
|
An empty object, called results, is created to store the processed data. |
|
|
Defines the required columns; that is node, parent, url, and id. |
|
|
Maps the columns to their types. |
|
|
Set to an array of objects, each representing a row of data with values for the columns defined earlier. |
|
|
The callback function is called with the results object as its argument, passing the processed data back to the function that called this one. |
The following screenshot illustrates this data source configuration in the Virtual tab.

This creates the menu structure as per the following table:
|
Node |
Parent |
URL |
ID |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Visualizations Demos |
|
#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162 |
1001 |
|
Products Demos |
|
#b206840b-2e64-4209-bacd-166c883928f |
1002 |
|
Component Demos |
|
#80c52499-cd0a-a1ca-46bb-178be3aaeed |
1003 |
|
Demo Visualize |
Visualizations Demos |
#53c5e521-2d14-4d6d-fe61-16ca42cea162 |
1004 |
|
Demo Health |
Products Demos |
#b206840b-2e64-4209-bacd-166c883928f |
1005 |
|
Demo Sensors |
Products Demos |
#c02f1251-9300-2c35-9efe-85a0b87665f4 |
1006 |
|
Data |
Component Demos |
#80c52499-cd0a-a1ca-46bb-178be3aaeed |
1007 |
|
Graph |
Component Demos |
#b58fe5e3-d02f-3130-2e53-5bddc0bbac3d |
1008 |
The first three values in the Node column are Visualizations Demos, Products Demos, and Component Demos. These are main menu items because their corresponding Parent column is empty.
The drop-down menu for any main menu item has that main menu as their parent. For example, Component Demos has two items in its drop-down menu; Data and Graph.
Views example
The example below shows a navigation menu in kdb Insights Enterprise Views.

The following code created this navigation menu.
JavaScript
function (source, callback) {
const results = {};
// source is an object representing a data source, with the following properties:
// columns: an array of column names, for example,
results.columns = [
"node",
"parent",
"url",
"id"
];
// meta: an object mapping column names to their kdb types
results.meta = {
"node": 0,
"parent": 0,
"url": 0,
"id": 7
};
// rows: an array of row objects, each one maps columns to values
results.rows = [
{"node":"Menu1","parent":"", "url":"#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542","id":1001},
{"node":"Menu2","parent":"","url":"#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542","id":1002},
{"node":"Menu3","parent":"","url":"#7d9afdf7-6915-45c6-9648-5f9c78e30827","id":1003},
{"node":"View1","parent":"Menu1","url":"#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542","id":1004},
{"node":"View2","parent":"Menu2","url":"#5a5b2cfd-6a7f-4815-9c00-eb97f8ff00ed","id":1005},
{"node":"View3","parent":"Menu2","url":"#7d9afdf7-6915-45c6-9648-5f9c78e30827","id":1006},
{"node":"View4","parent":"Menu3","url":"#7901772c-5cbf-404e-9fe9-672238e55a0d","id":1007},
{"node":"View5","parent":"Menu3","url":"#b846675c-3df7-42b3-b248-8fe3e073a616","id":1008},
{"node":"View5","parent":"Menu3","url":"#8928ff46-e47d-496d-8d07-129540e2c1da","id":1008}
];
// you can perform operations on the source, generate values or fetch remote data using javascript
// when you are done pass an object in the same format as source to the callback function to return your data
_.each(results.rows, r => {
if (r.url.indexOf("#") === 0) {
r.url = ($("kx-report-editor").length ? "view" : $("kx-report-viewer").length ? "view/share" : "") + r.url;
}
});
callback(results);
}This JavaScript example contains the following elements:
|
Element |
Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Defines an anonymous function that takes two parameters: source and callback. |
|
|
An empty object, called results, is created to store the processed data. |
|
|
Defines the required columns; that is node, parent, url, and id. |
|
|
Maps the columns to their types. |
|
|
Set to an array of objects, each representing a row of data with values for the columns defined earlier. |
|
|
The callback function is called with the results object as its argument, passing the processed data back to the function that called this one. |
|
|
This section checks each row, and if the URL starts with "#", it adds "view" or "view/share" to the beginning of the URL based on whether certain elements are present in the page. |
The following screenshot illustrates this data source configuration in the Virtual tab.

This creates the menu structure as per the following table:
|
Node |
Parent |
URL |
ID |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Menu1 |
|
view#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542 |
1001 |
|
Menu2 |
|
view#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542 |
1002 |
|
Menu3 |
|
view#7d9afdf7-6915-45c6-9648-5f9c78e30827 |
1003 |
|
View1 |
Menu1 |
view#4991a5d8-2b08-4247-a56c-d04e3a12c542 |
1004 |
|
View2 |
Menu2 |
view#5a5b2cfd-6a7f-4815-9c00-eb97f8ff00ed |
1005 |
|
View3 |
Menu2 |
view#7d9afdf7-6915-45c6-9648-5f9c78e30827 |
1006 |
|
View4 |
Menu3 |
view#7901772c-5cbf-404e-9fe9-672238e55a0d |
1007 |
|
View5 |
Menu3 |
view#b846675c-3df7-42b3-b248-8fe3e073a616 |
1008 |
|
View5 |
Menu3 |
view#8928ff46-e47d-496d-8d07-129540e2c1da |
1008 |
The first three values in the Node column are Menu1, Menu2, Menu3. These are main menu items because their corresponding Parent column is empty.
The drop-down menu for any main menu item has that main menu as their parent. For example, Menu2 has 2 items in its drop-down menu; View2 and View3.
Navigation Menu properties
The following sections provides details on how to configure the properties of the Navigation Menu component.
Basics
Open the Basics properties on the right and configure the properties described in the following table.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Enter a name for the component. |
|
Data Source |
Configure the data source, which defines the menu structure. |
|
Font Size |
Select a font size for the menu items. |
Node
These properties map your data source columns to the elements of the navigation menu. Configure the Nodes to map each of the menu elements to the columns in your data source. This is only required if your column names differ from the default columns; Node, Parent, URL, and ID.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Node |
The default columns are Node, Parent, URL, and ID. If you use these column names in your data source, they are automatically mapped to the correct default columns here. If you use alternative column names, map them here by selecting your column name and mapping it to a default value.
Note These drop-downs are populated after you setup the data source.
|
|
Parent |
|
|
URL |
|
|
ID |
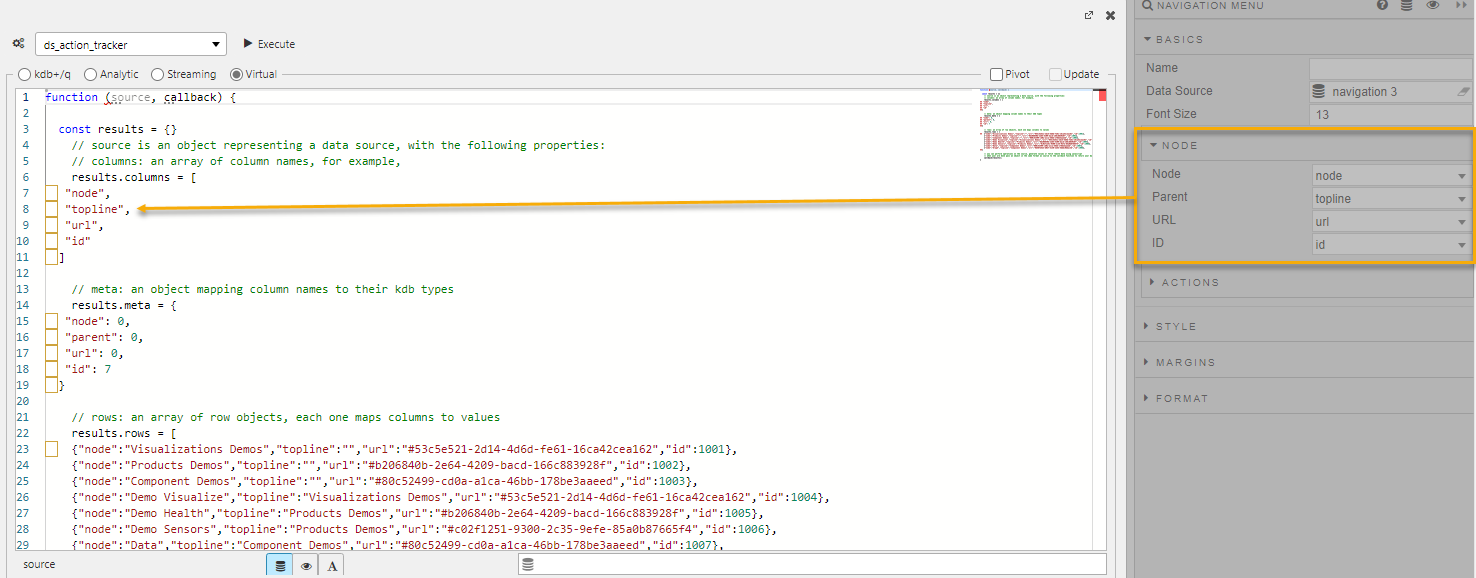
For example, if you define TopLine as the top-level menu item in your data source, map it to Parent in the Node properties, as shown below.
Actions
Refer to Actions documentation for common settings.
Style, Margins, Format
Refer to Style documentation for common settings.