Graph
This page describes how to set up and configure the Graph component .
The Graph component presents an interactive display that can show the relationships between nodes. A node is an element in the graph that represents an object, such as a noun. An edge shows the relationship between two nodes in the graph. The Graph component can present these details as labelled nodes with connections or organized in hierarchical form.
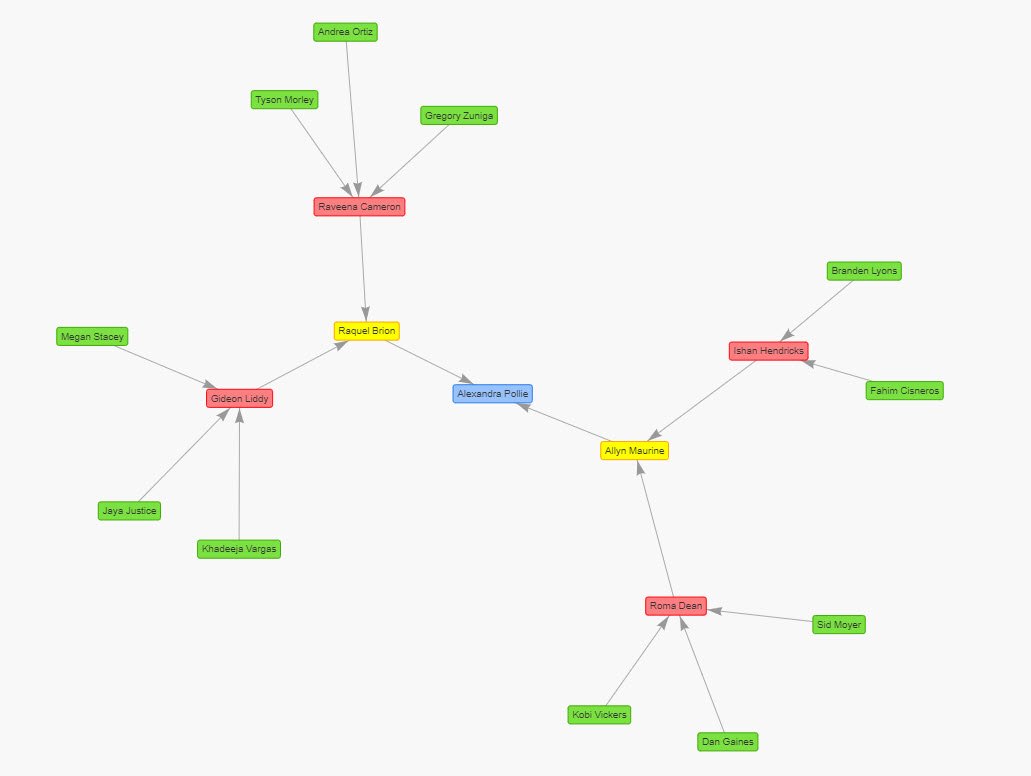
The following screenshot provides an example graph using physics to show to whom different positions in a company report to.

The next example shows a hierarchical graph showing direct managers for positions within a company.

This page provides information on the following:
Set up a Graph
To set up a Graph component, click-and-drag the component into the workspace and configure the following:
-
In the Design View, click and drag the Graph component onto the workspace.

-
Within the Graph component, click on the label "Click to populate Nodes Data Source" or from the Properties Panel, expand the Data section, and click on the Source input field from the Nodes section to open the Data dialog.
-
Create or select a data source. This data source must have at least two columns to identify the node's text label and unique identifier. Optional properties, such as Level, Group, Mass or Custom Shape can be defined for each node.
-
Assign a column from the Nodes data source to the Label property.
-
Assign a column from the Nodes data source to the ID property.
-
Within the Graph component, click on the label "Click to populate Edges Data Source" or from the Properties Panel, expand the Data section, and click on the Source input field from the Edges section to open the Data dialog.
-
Create or select a data source. This data source is used to specify a connection between a pair of nodes using their unique identifier values. Each endpoint for a connection (edge) comes from a data source column. A unique identifier for each edge can be optionally specified.
-
Assign a column from the Edges data source to the From property.
-
Assign a column from the Edges data source to the To property.
Refer to a Graph component properties described in the next section for details on additional properties.
Graph component properties
The following sections provides details on how to configure the properties of the Graph component.
Basic
The Basic properties, shown in the following image, are described below.

|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Name |
Enter a name for the component. |
|
Selected Node |
Specify a View State Parameter to store the unique identifier of the selected node(s). This is optional.
Selecting a node: In Preview mode or the End-User version of the Dashboard, click on a node to assign a value to the Selected Node view state parameter. Use the Control key to make multiple selections. |
|
Selected Edge |
Specify a View State Parameter to store the unique identifier of the selected edge(s). This is optional.
Selecting an edge: In Preview mode or the End-User version of the Dashboard, click on an edge to assign a value to the Selected Edge view state parameter. Use the Control key to make multiple selections. |
Data
This section identifies data source attributes that are used to define the nodes and edges. The following image shows the Graph's property section for Data.

Nodes
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Source |
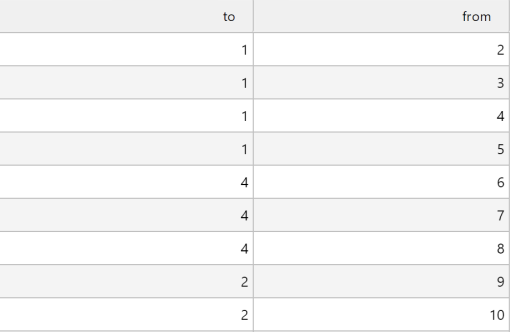
The Data Source must have at least two columns to define the node's unique identifier (ID) and text label. Each row in the data source is used to define a node.
Data source results with the node ID and label |
|
Label |
Data source column containing the text to be used for the nodes. |
|
ID (must be unique) |
Data source column containing the unique ID for the nodes. |
|
Level (optional) |
Data source column containing a numerical value that is used to specify the hierarchical position of the node.
The following example shows a hierarchical layout oriented from left to right, with an added illustration to show the levels in pink
|
|
Group (optional) |
Data source column containing a group name to be associated with the node. As many as 21 superseding color sets are used to identify nodes in the same group.
The following example illustrates a graph showing nodes belonging to 1 of 4 groups.
|
|
Mass (optional) |
Data source column used to specify the mass of the individual nodes. If no value is specified or the value is non-numeric, the minimum value of 1 is used. Larger values increase the repulsion effect for that specific node.
To see the effect, this property requires Physics to be enabled.
In the example below, the node labeled 'Alexandra Pollie' has more mass and therefore, the repulsion effect is greater for that specific node, resulting in its further distance.
|
Node Color Sources
The data source for Nodes can specify the color attributes for each node. This method overrides the colors defined in the Default Node Style section.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
Data source column containing the background color of the nodes. |
|
Border Color |
Data source column containing the border color of nodes. |
Selected Node Color
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
Data source column containing the background color of the selected nodes. |
|
Border Color |
Data source column containing the border color of the selected nodes. |
Node Hover Color
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
Data source column containing the background color of the nodes when the user mouses over them. |
|
Border Color |
Data source column containing the border color of the nodes when the user mouses over them. |
Shape
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Custom Shape |
The data source column containing the form the nodes takes. For example, circle, database, diamond, square, hexagon, triangle. |
Edges
The edges show connections between nodes.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Source |
This Data Source must return the columns to define the edge endpoints for the connection drawn between the From and To nodes.
The following example shows data source results with To and From columns.
|
|
From |
Data source column containing the node ID for the start of the edge. |
|
To |
Data source column containing the node ID for the end of the edge. |
|
ID (optional) |
Data source column containing the unique ID for the edges. |
Default Node Style
The following properties, shown in the image below, are used to style the nodes.

The border properties are described in the following table.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Border Width |
Specifies the thickness of the node border. |
|
Selected Border Width |
Specifies the thickness of the selected node border. |
Color
The following are the color properties of a node. Any of these color properties can be overridden if a data source column is used to define that color property in the Node Color Sources section.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
Specifies the background color of the nodes. |
|
Border Color |
Specifies the border color of the nodes. |
Selected color
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
The background color of a node when it is selected. |
|
Border Color |
The border color of a node when it is selected. |
Hover color
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Background Color |
The background color of the nodes when the user mouses over them. |
|
Border Color |
The border color of the nodes when the user mouses over them. |
Default Edge Style
The following properties, shown in the image below, are used to style the edges.

The edge width properties are described in the following table.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Edge Width |
Specifies the thickness of the edge. |
|
Selected Edge Width |
Specifies the thickness of the selected edge. |
Arrows
Arrowheads can be added to the edge endpoints. The properties are described below.
To
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enabled |
When checked, an arrowhead is added to the To side of the edge. |
|
Arrow Size |
Specifies the size of the To arrowhead. |
From
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enabled |
When checked, an arrowhead is added to the From side of the edge. |
|
Arrow Size |
Specifies the size of the From arrowhead. |
Color
The following properties are used to configure the color of the edges.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Edge Color |
Specifies the color of the edge. |
|
Selected Edge Color |
Specifies the color of the selected edge. |
|
Opacity |
Defines the opacity of the edge with a value between 0 (transparent) and 1 (opaque). |
User Interaction
The User Interaction properties define how the user can interact with the graph. The properties are described in the table below.

|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Draggable Nodes |
Allows the user to reposition nodes via click and drag.
|
|
Draggable View |
Allows the user to pan the graph image in different directions by clicking and dragging on an empty space in the graph. |
|
Select Connected Edges |
Selects all edges for the selected node(s).
|
Physics
This section contains properties used to influence and define the physical behavior of objects in the graph.

These properties are described in the following table.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable Physics |
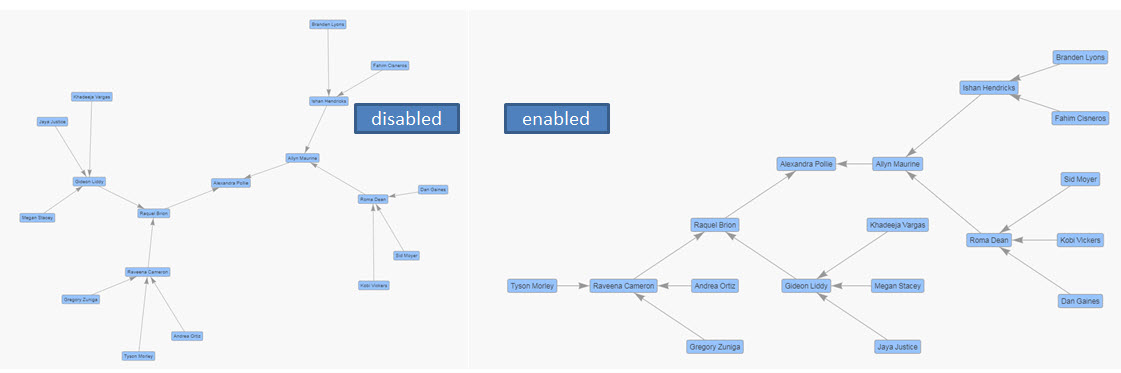
When enabled, a physics algorithm is used to create the graph by simulating the physical properties of nodes and edges while also being affected by gravity.
The image above shows graph behavior without physics, and the image below shows the graph with physics enabled.
|
|
Max Steps Before Rendering |
A step refers to a time duration where the position of one or more nodes may be affected by various forces (for example, gravity, edge stiffness) and potentially traveling some distance given its velocity. This property value refers to the maximum number of simulated steps taken before the graph is visible. |
|
Halt Physics After Rendering |
This property determines whether physics continue after the graph has been rendered.
|
|
Minimum Graph Speed |
Once the speed of all the nodes is less than or equal to the minimum graph speed no further steps are taken to affect the position of the nodes. |
|
Maximum Node Velocity |
The maximum speed at which the nodes are allowed to move. This is a speed limit for the nodes. |
|
Anti-Gravity Constant |
This value is used in a formula to quantify the effect of gravity for the nodes as if it were a repelling force. It represents the gravitational constant as a negative value. Higher values increase the repulsion effect and lower values approaching zero reduce it. |
|
Central Gravity Attractor |
A force pulling the entire network towards the center of the graph.
|
|
Edge Length |
The edges of the graph are modelled as springs and this value determines their length at rest. |
|
Edge Stiffness |
The edges of the graph are modelled as springs. A larger value increases the minimum force required to affect the length of the edge. |
Warning
When Physics and Hierarchical Layout are both enabled, the node behavior associated with the hierarchical layout overrides the physics simulation.
Tooltips
The nodes in the graph can have tooltips. These properties are shown in the image below.

The Tooltips Property section is described in the following table.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Show Tooltip |
When checked, a tooltip is presented to the user when the mouse hovers over a node. |
|
Template |
See Templates for full details. |
Actions
See Actions for full details.
Layout
The Layout properties, shown in the image below, are used to affect the arrangement of nodes and edges in the graph.

|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Random Layout Pattern |
When checked, the initial position of the nodes and edges are different each time a new start position is required. Hierarchical layouts are not affected by this setting.
The images above and below are for separate occurrences of the same data being used to render a graph with the Random Layout Pattern property checked.
|
|
Layout Pattern |
This numerical value is used to determine the initial layout of the graph. The results are consistent provided the data is unchanged. This does not apply to hierarchical layouts.
|
|
Group Zoom Threshold |
The graph component automatically zooms in/out when the window is resized and during the initial rendering so that all graph elements are within the visible boundary. The user can also manually zoom in/out by using the mouse wheel or the touchpad pinch-zoom input method. Zooming in increases the zoom level, and zooming out decreases it. The Group Zoom Threshold is a number between 0 and 100 and it is used to identify a point for when the graph automatically transitions between showing individual nodes versus the individual groups for those nodes (groups appear as a circle shape).The graph's current zoom level is compared to the Group Zoom Threshold so that:
For example, for a given zoom level, if groups are displayed but the preference is to see individual nodes instead, the value of the Group Zoom Threshold must be reduced. Note Use of the Group Zoom Threshold requires the Group property to be defined.
|
Hierarchical
The following properties can be configured when using a hierarchical layout.
|
Property |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Enabled |
When enabled, the nodes are arranged to show a parent-child relationship based on the node's Level attribute.
|
|
Level Separation |
Defines the height in pixels between levels. |
|
Node Spacing |
Defines the width in pixels between nodes. |
|
Direction |
This property is used to indicate the direction of the hierarchy as they appear starting from the Top level to the Bottom level. The options are: Left to Right, Right to Left, Up to Down, and Down to Up. |
Style, Margins, Format
See Style for full details of common settings.