Readers
This page explains how to set up reader operators, for kdb Insights Enterprise pipelines, using the Web Interface.
Reader operators enables both streaming and batch data to be ingested into kdb Insights Enterprise.
Note
Both q and Python interfaces can be used to build pipelines programmatically. See the q and Python APIs for details.
The pipeline builder uses a drag-and-drop interface to link together operators within a pipeline. For details refer to the Building a pipeline guide.
The following readers are available:
Callback
Use this reader to receives data from a callback from the local process or over IPC.
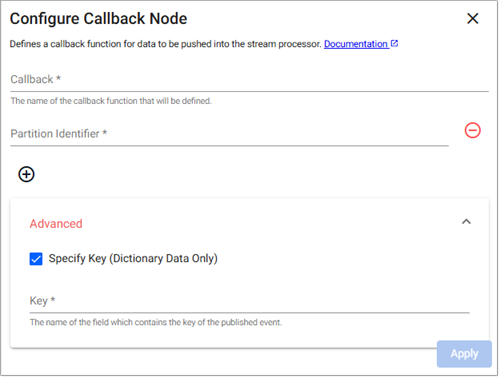
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Callback
|
name |
description |
default |
required |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Callback |
The name of the callback function where data is received. |
None |
Y |
|
Add Partition Identifiers |
Click + to add a Partition Identifier field. |
None |
N |
|
Enable Message Replay (Beta Feature) |
If enabled messages that arrived after the last checkpoint are replayed on recovery. This is off by default for performance reasons. |
N |
N |
|
Specify Key |
This is used to specify a key field for the event, and can only be checked for dictionary events. When checked the Key field is displayed. |
Unchecked |
N |
|
Key |
Name of the field which contains the key of the published event. Only available when Specify Key is checked. |
None |
N |
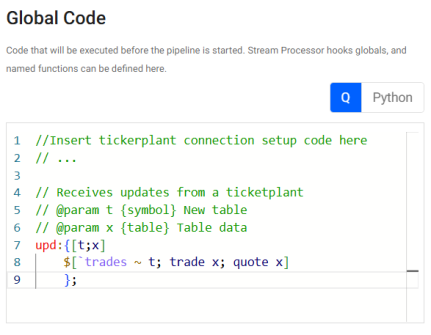
Example: Publishing from a tickerplant
A tickerplant is a message bus that typically sends data to subscribers in the form of (table; data). In this example, we subscribe to a tickerplant with a trades and a quotes table with independent callback readers.
-
Drag out a callback reader and set the name to be Callback name to
trade. -
Drag out a second callback reader and set the name to be Callback name to
quote. -
Setup the following global code, for establishing a connection to the tickerplant and dispatching to the appropriate callback function based on the table name.
q
Copy//Insert tickerplant connection setup code here
// ...
// Receives updates from a ticketplant
// @param t {symbol} New table
// @param x {table} Table data
upd:{[t;x]
$[`trades ~ t; trade x; quote x]
};
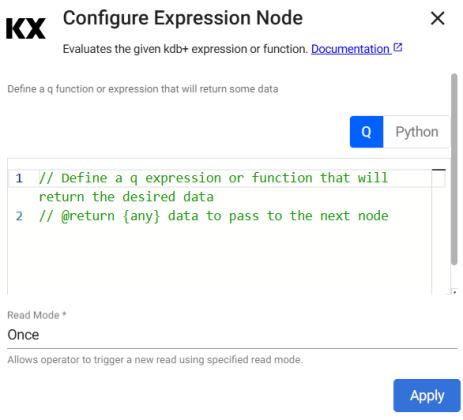
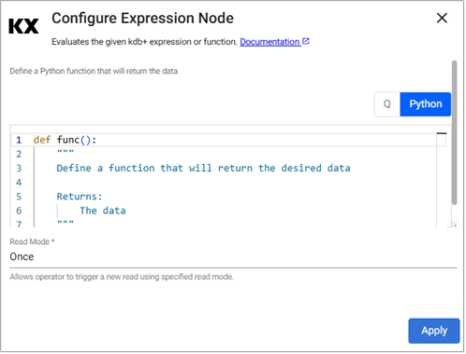
Expression
This reader runs a kdb+ expression.
q Expression operator
Python Expression operator
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Expression
The expression reader executes a snippet of kdb+ code and passes the result into the pipeline. This operator is mostly used for testing pipelines with mock data.
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Expression |
A snippet of kdb+ code or a Python function to be evaluated. The last statement in this code snippet is treated as the data source. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Read Mode |
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of |
|
|
Period |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
|
|
Set Start Time |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
Unchecked |
|
Start Time |
The time the initial read is triggered. |
Today |
Note
Trigger URL
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The
The following screenshot shows the Trigger Read properties displayed when Trigger Mode is set to Timer.
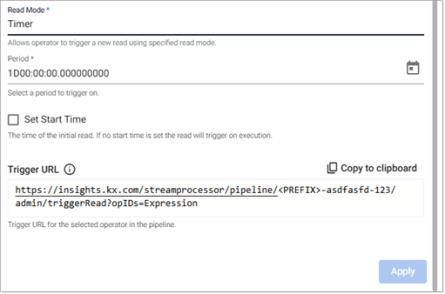
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.
Example: Generating data
The code snippet below generates a sample table with 2000 rows for testing:
q
Python
q
n:2000;
([] date:n?(reverse .z.d-1+til 10);
instance:n?`inst1`inst2`inst3`inst4;
sym:n?`USD`EUR`GBP`JPY;
num:n?10)
Python
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from datetime import datetime,timedelta
def gen():
n=2000
dates = [datetime.today().date() - timedelta(10-i,0,0) for i in range(10)]
return pd.DataFrame({'date' : np.random.choice(dates,n),
'instance' : np.random.choice(["inst1","inst2","inst3","inst4"],n),
'sym' : np.random.choice(["EUR","USD","GBP","JPY"],n),
'num' : np.random.randint(0,10,n)})
Google Cloud Storage
This reads an object from Google Cloud Storage.
There are two versions of the reader:
-
Version 1: The original and default version.
-
Version 2: Supports parallel file downloads, significantly increasing throughput during processing. This is the recommended option.
To change the operator version, click Select Version and select either Version 1 or Version 2.
Information
Changing versions overwrites operator configuration
Pipelines built using Version 1 of this operator continue to use that version unless you explicitly switch to Version 2.
If you change operator versions, the configuration fields specific to Version 2 are blank and must be set up manually. The existing Version 1 configuration is overwritten. The new configuration is applied only after you click Apply.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Google Cloud Storage
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Click the Version 2 or Version 1 tab below to view the operator configuration options available for each version.
Version 2
Version 1
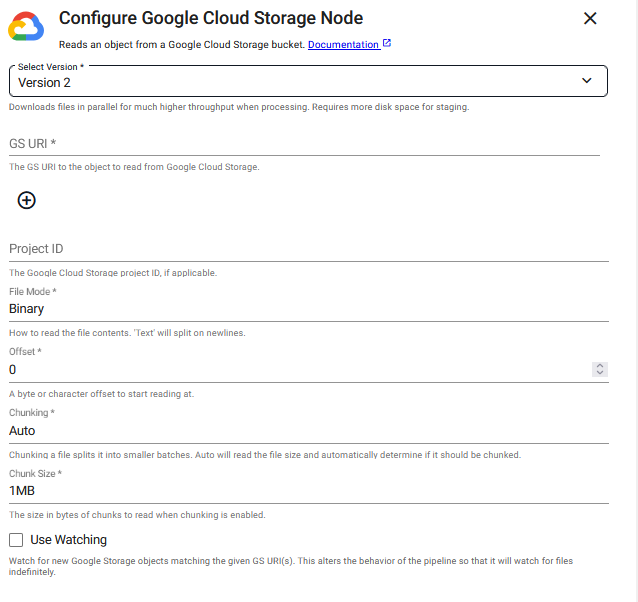 .
.
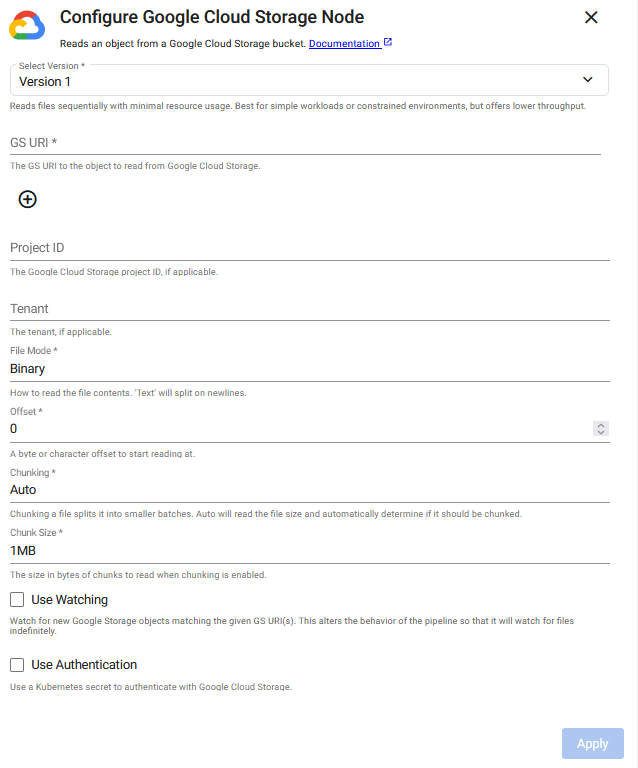 .
.
Information
Watching
Pair this with a glob pattern for the Path, otherwise new files are not detected when watching. The pipeline polls by the selected method at the selected frequency and reads the matching files once they become available. The reader continually watches for new files, matching the file path provided using the watch method.
When using Watching, the pipeline continues watching until there is manual intervention to finish the pipeline.
Warning
Watching should not be used with a Database Writer using the direct write option
When using Watching, it is not possible to pair this with a Database Writer using direct write since it relies on a definitive finish point, which is not guaranteed when using this option.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
V1 |
V2 |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Path |
Click the + button to add one or more Cloud Storage URIs to read from a Google cloud storage bucket. Glob patterns are supported. |
✔ |
✔ |
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
V1 |
V2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Project ID |
Google Cloud Storage Project ID, if applicable. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Tenant |
The authentication tenant, if applicable. |
|
✔ |
❌ |
|
File Mode |
The file read mode. Setting the file mode to |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Offset |
A byte or character offset to start reading at. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunking |
Splits file into smaller batches. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunk Size |
File size of chunks when chunking is enabled. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Use Watching |
Watch for new Google Storage objects matching the given Cloud Storage URI(s). |
No |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Method |
Method used to watch for new files. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Frequency |
Frequency of timer polling. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Use Authentication |
Enable Kubernetes secret authentication. |
No |
✔ |
❌ |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret to authenticate with Google Cloud Storage. Only available if |
No |
✔ |
❌ |
Google Cloud Storage Authentication
Google Cloud Storage Authentication uses Kurl for credential validation.
Environment variable authentication
To setup authentication using an environment variable, set GOOGLE_STORAGE_TOKEN in Google's gcloud CLI
Bash
gcloud auth print-access-token
Kubernetes secrets for authentication
A Kubernetes secret may be used to authenticate files. This secret needs to be created in the same namespace as the kdb Insights Enterprise install. The name of that secret is then used in the Kubernetes Secret field when configuring the reader.
To create a Kubernetes secret with Google Cloud credentials:
Bach
kubectl create secret generic SECRET_NAME DATA
Note
SECRET_NAME is the name of the secret used in the reader. DATA is the data to add to the secret; for example, a path to a directory containing one or more configuration files using --from-file or -from-env-file flag, or key-value pairs each specified using --from-literal flags.
HTTP
This reader requests data from an HTTP(S) endpoint.
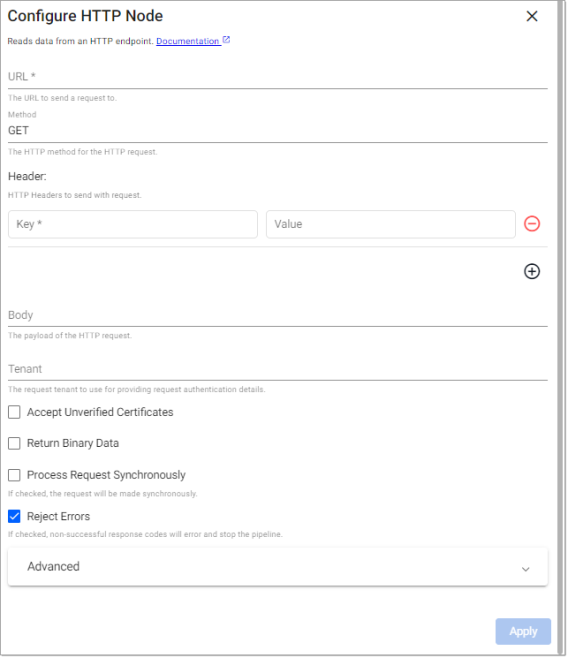
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: HTTP
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
URL |
The URL to send the request to. The URL must include the protocol ( |
|
|
Method |
The method to use for sending the HTTP request. This must be one of |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Body |
The payload of the HTTP request. The body of the request is any content that needs to be included when sending the request to the server. |
|
|
Header |
A map of header fields to send as part of the request. |
|
|
Tenant |
The request tenant to use for providing request authentication details. |
|
|
Accept Unverified Certificates |
When checked, any unverified server SSL/TLS certificates is considered trustworthy |
No |
|
Return Binary Data |
When checked, payload is returned as binary data, otherwise payload is treated as text data. |
No |
|
Process Request Synchronously |
When checked, a synchronous request blocks the process until the request is completed. Default is an asynchronous request. |
No |
|
Reject Errors |
When checked, a non-successful response generates an error and stop the pipeline. |
Yes |
|
Read Mode |
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of |
|
|
Period |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
|
|
Set Start Time |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
Unchecked |
|
Start Time |
The time the initial read is triggered. |
Today |
Note
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.
Advanced Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Follow Redirects |
When checked, any redirects are automatically followed up to the |
|
|
Max Redirects |
The maximum number of redirects to follow before reporting an error. |
|
|
Max Retry Attempts |
The maximum number of times to retry a request that fails due to a timeout. |
|
|
Timeout |
The duration in milliseconds to wait for a request to complete before reporting an error. |
|
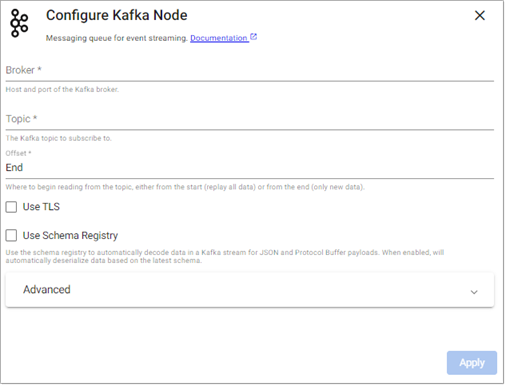
Kafka
This reader consumes data from a Kafka topic.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details : Kafka
Kafka is a scalable streaming message queue for processing streaming data. Refer to the Kafka ingestion example for details about setting ingesting from Kafka.
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Broker |
Location of the Kafka broker as host:port. If multiple brokers are available, they can be entered as a comma separated list. |
|
|
Topic |
The name of the Kafka topic to subscribe to. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Offset |
Read data from the |
|
|
Use TLS |
Enable TLS for encrypting the Kafka connection. When selected, certificate details must be provided with a Kubernetes TLS Secret |
No |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret that is already available in the cluster and contains your TLS certificates. Only available if Use TLS is selected. |
|
|
Certificate Password |
TLS certificate password, if required. Only available if Use TLS is enabled. |
|
|
Use Schema Registry |
Use the schema registry to automatically decode data in a Kafka stream for JSON, Avro and Protocol Buffer payloads. When enabled, automatically deserializes data based on the latest schema. |
No |
|
Registry |
Kafka Schema Registry URL. Only available if Use Schema Registry is selected. |
|
|
As List |
Set to true for Kafka Schema Registry messages to omit field names when decoding Protocol Buffer schemas, and instead return only the list of values. Only available if Use Schema Registry is selected. |
No |
Note
Refer to this guide from Kubernetes for more details on setting up TLS Secrets.
Advanced Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Retry Attempts |
The maximum number of retry attempts allowed. |
|
|
Retry Wait Time |
The amount of time to wait between retry attempts. |
|
|
Poll Limit |
Maximum number of records to process in a single poll loop. |
|
|
Use Advanced Kafka Options |
Set to true and click the + button to add one or more key-value pairs, where the keys are Kafka configuration properties defined by librdkafka. |
|
Note
Allows more flexible options for security protocol configuration or changes to fetch intervals, as seen when subscribing to an Azure Event Hub Kafka connector.
Note
The Kafka reader automatically commits offsets when reading from a broker.
This is essential for exactly once semantics and fault tolerance.
The error Local: Waiting for coordinator occur when attempting to commit
offsets if you do not have sufficient group permissions. The broker should be configured so that
the user has group Describe permissions. Since The Kafka Reader generates a
random group ID, ensure the user is permissioned for all group names on the broker.
kdb Insights Database
Use this reader to read from a kdb Insights Database.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: kdb Insights Database
The configuration options vary depending on the Query Mode you select.
Note
The SQL option is not available
Get Data API
The settings for reading from kdb Insights Database using Get Data API are described below.
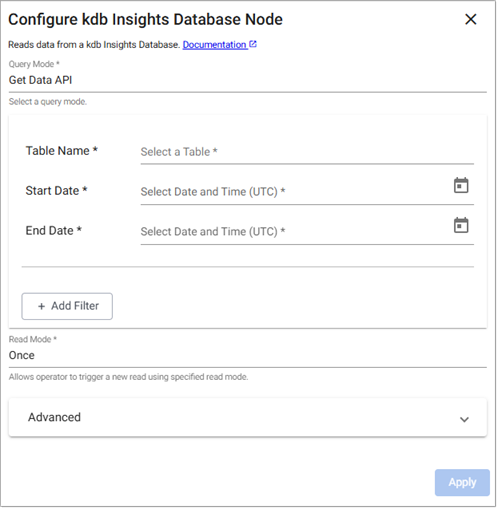
-
Enter values for the following required parameters.
Parameter
Description
Table Name
The name of the table data is to be retrieved from.
Start Date
The inclusive start time of the period of interest.
End Date
The exclusive end time of the period of interest.
-
To add optional filters, click + Add Filter and click Add Function to select one of the filter options.
Additional options are displayed depending on the filter option selected.
Filter option
Description
filter
A function that returns true for rows to include.
filter by label
When multiple databases each have a table matching the table name, filtering by label can select a subset of those.
sort
A column to sort by (ascending).
define aggregation
Apply an aggregation over a column for the rows matching the query, assigning the result to a new column.
group aggregation by
Group the result of the query by the specified column before running the aggregation.
-
Optional Parameters:
name
description
default
Read Mode
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of
Once,API,TimerOncePeriod
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to
Timer, specifies the period to trigger the read on.1D00:00:00Set Start Time
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to
Timer, sets the time of the initial read. When unchecked the read triggers on execution. When checked a Start Time parameter is displayed.Unchecked
Start Time
The time the initial read is triggered.
Today
Note
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.
-
Click Advanced to optionally enter values for the following.
Advanced Parameter
Description
Default
Retry Attempts
Maximum number of retry attempts allowed.
5Retry Wait Time
Wait time between retry attempts.
2 seconds
UDA
The settings for reading from kdb Insights Database using UDAs are described below. See UDAs for details on how these analytics are created and loaded to kdb Insights Enterprise.
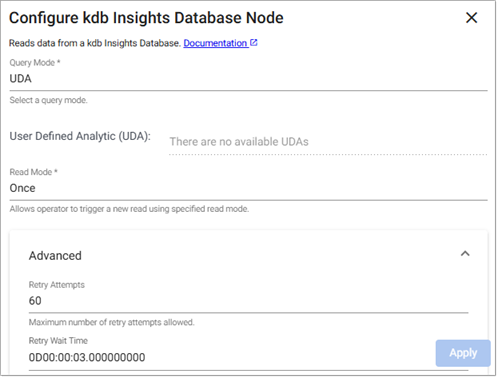
-
Select a User Defined Analytic(UDA) from the list of available UDAs.
-
Optional Parameters:
name
description
default
Read Mode
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of
Once,API,TimerOncePeriod
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to
Timer, specifies the period to trigger the read on.1D00:00:00Set Start Time
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to
Timer, sets the time of the initial read. When unchecked the read triggers on execution. When checked a Start Time parameter is displayed.Unchecked
Start Time
The time the initial read is triggered.
Today
Note
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.
-
Click Advanced to optionally enter values for the following.
Advanced Parameter
Description
Default
Retry Attempts
Maximum number of retry attempts allowed.
5Retry Wait Time
Wait time between retry attempts.
2 seconds
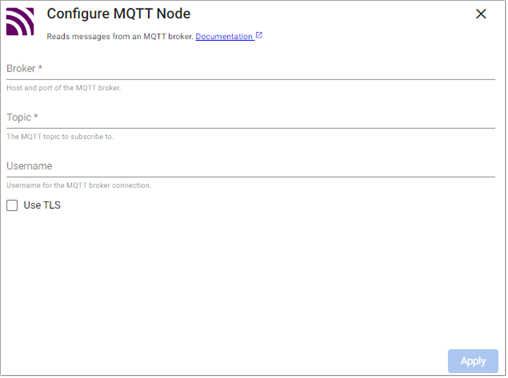
MQTT
Use this reader to subscribe to an MQTT topic.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: MQTT
Read messages from an MQTT broker. MQTT is a lightweight, publish-subscribe, machine to machine network protocol for message queuing service. It is designed for connections with remote locations that have devices with resource constraints or limited network bandwidth.
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Broker |
Location of the MQTT broker as |
|
|
Topic |
The name of the MQTT topic to subscribe to. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Username |
Username for the MQTT broker connection. |
|
|
Use TLS |
Enable TLS for encrypting the Kafka connection. When selected, certificate details must be provided with a Kubernetes TLS Secret |
No |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret that is already available in the cluster and contains your TLS certificates. Only available if Use TLS is selected. |
|
|
Certificate Password |
TLS certificate password, if required. Only available if Use TLS is selected. |
|
Note
Refer to this guide from Kubernetes for more details on setting up TLS Secrets
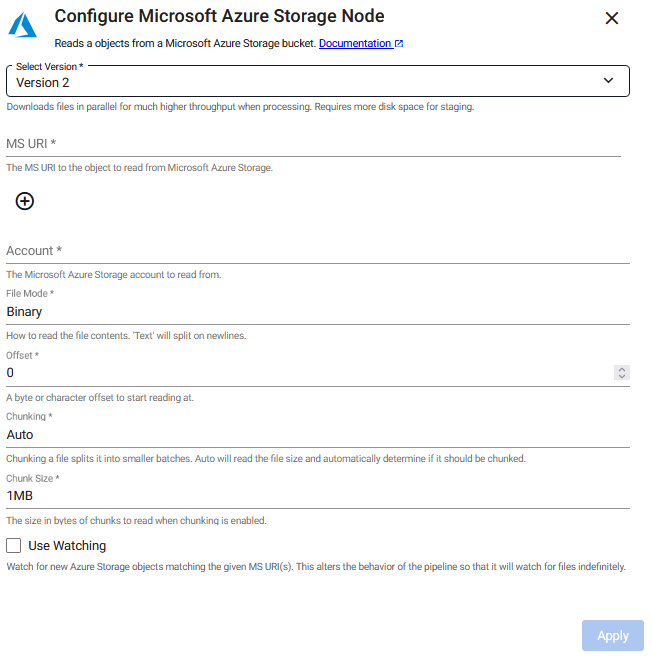
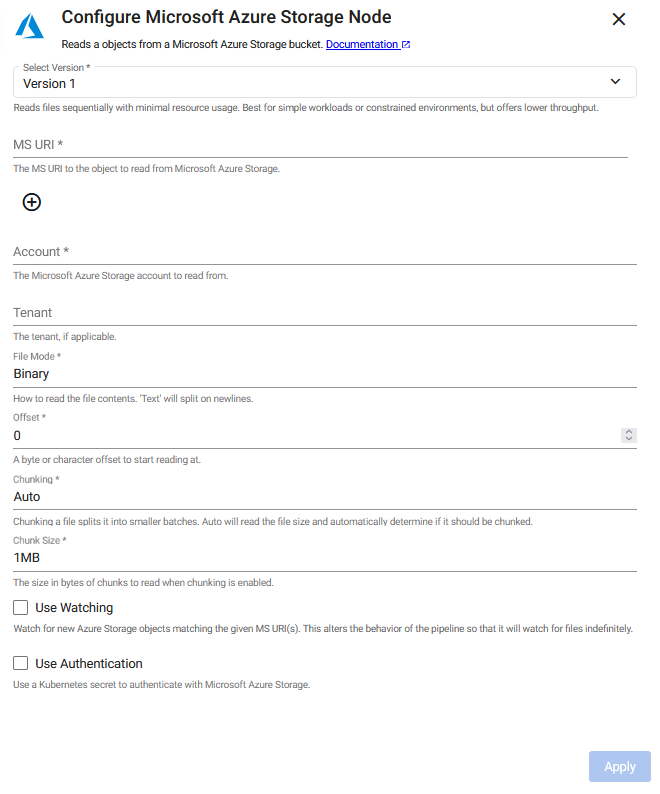
Microsoft Azure Storage
This reads an object from Microsoft Azure Storage. There are two versions of the reader:
-
Version 1: The original and default version.
-
Version 2: Supports parallel file downloads, significantly increasing throughput during processing. This is the recommended version
To change the operator version, click Select Version and select either Version 1 or Version 2.
Note
Changing versions overwrites operator configuration
Pipelines built using Version 1 of this operator retain this version unless you change it. If you change operator versions, the fields of the Version 2 screen are blank and the Version 2 fields have to be configured. The Version 1 current configuration is overwritten and the new configuration is applied when you click Apply. You are notified and asked to confirm this action.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Microsoft Azure Storage
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Click the Version 2 or Version 1 tab below to view the operator configuration options available for each version.
Version 2
Version 1
Note
Pair this with a glob pattern for the Path or else new files are not detected when watching. The pipeline polls by the selected method at the selected frequency and reads matching files once they become available. The reader continually watches for new files matching the file path provided using the watch method.
When using watching the pipeline continues watching until there is manual intervention to finish the pipeline.
Note
Watching should not to be used with a Database Writer using the direct write option
When using the Watching option it is not possible to pair this with a Database Writer using direct write since direct write relies on a definitive finish point which is not guaranteed when using this option.
Required Parameters:
|
NAme |
description |
default |
V1 |
V2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Path |
Click the + button to add one or more Blob Storage URIs to read from an Azure cloud storage bucket. Glob patterns are supported. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Account |
The name of the Azure Storage Account hosting the data. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
V1 |
V2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tenant |
The authentication tenant, if applicable. |
|
✔ |
❌ |
|
File Mode |
The file read mode. Setting the file mode to |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Offset |
A byte or character offset to start reading at. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunking |
Splits file into smaller batches. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunk Size |
File size of chunks when chunking is enabled. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Watch for new Azure Storage objects matching the given URI(s). |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
|
Method |
Method used to watch for new files. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Frequency |
Frequency of timer polling. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Use Authentication |
Enable Kubernetes secret authentication. |
No |
✔ |
❌ |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret to authenticate with Google Cloud Storage. Only available if |
|
✔ |
❌ |
Microsoft Azure Authentication
Microsoft Azure Storage Authentication uses Kurl for credential validation.
Environment variable Authentication
To set up authentication with an environment variable, set AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT to the name of the storage account to read from, and AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY to the one of the keys of the account. Additional details on shared keys usage available here.
Learn more about Shared Keys.
Kubernetes secrets for authentication
A Kubernetes secret may be used to authenticate files. This secret needs to be created in the same namespace as the kdb Insights Enterprise install. The name of that secret is then used in the Kubernetes Secret field when configuring the reader.
To create a Kubernetes secret with Azure credentials:
Bash
kubectl create secret generic --from-literal=token="$AZURE_STORAGE_TOKEN" ms-creds
Learn more about Kubernetes Secrets.
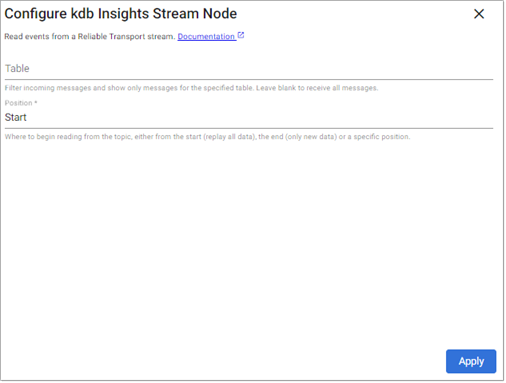
kdb Insights Stream
This reads data from a kdb Insights Stream.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: kdb Insights Stream
Insights streams
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Table |
Filter incoming messages to show only messages for the specified table. If no filter is provided, all messages in the stream are consumed. |
|
|
Position |
Position in the stream to replay from. Options are |
|
|
Replay Position |
When Specific Position is selected, this is used to set the integer stream position |
0
|
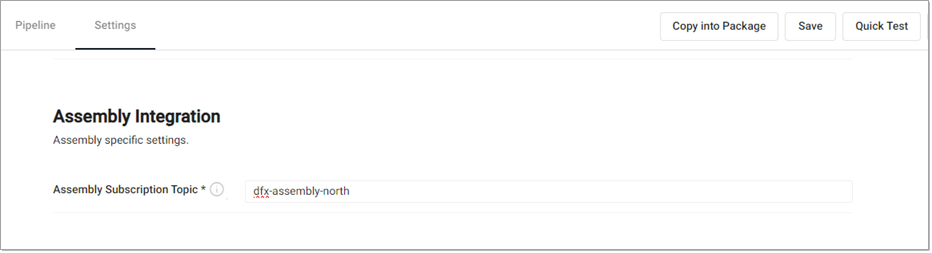
To read data from a stream, an assembly must be provided. This is done prior to pipeline deploy time. Visit the Settings tab in the pipeline editor and fill in the Assembly Integration field with the assembly name and topic name.
Amazon S3
This reads an object from Amazon S3.
There are two versions of the reader:
-
Version 1: The original and default version.
-
Version 2: Supports parallel file downloads, significantly increasing throughput during processing. This is the recommended version.
To change the operator version, click Select Version to select either Version 1 or Version 2.
Note
Changing versions overwrites operator configuration
Pipelines built using Version 1 of this operator retain this version unless you change it. If you change operator versions, the fields of the Version 2 screen are blank and the Version 2 fields have to be configured. The Version 1 current configuration is overwritten and the new configuration is applied when you click Apply. You are notified and asked to confirm this action.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Amazon S3
Information
This readers are also available in the import wizard.
Click the Version 2 or Version 1 tab below to view the operator configuration options available for each version.
Version 2
Version 1
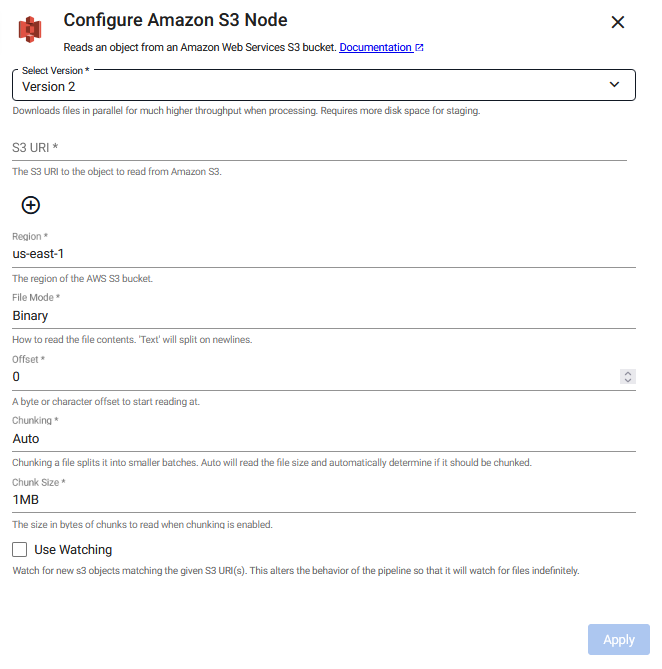
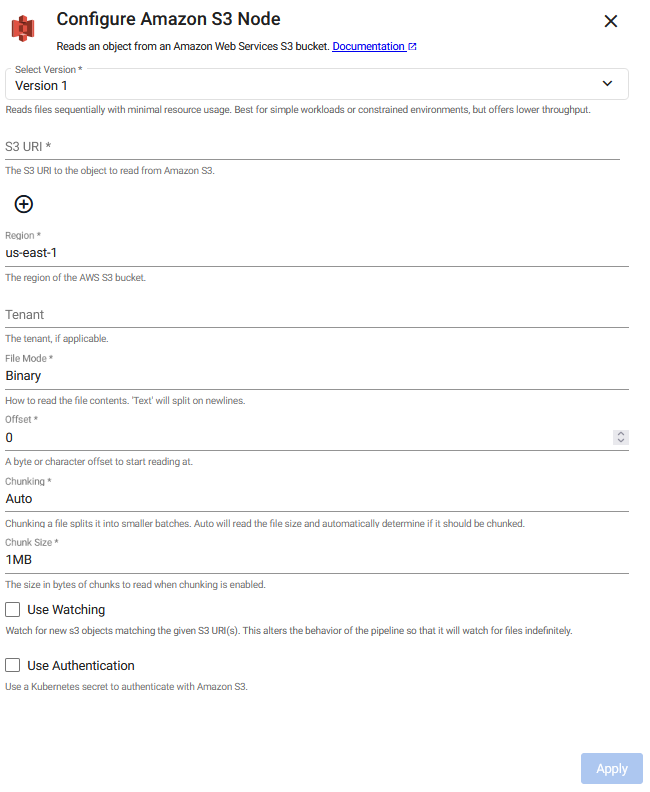
Note
Pair this with a glob pattern for the Path or else new files are not detected when watching. The pipeline polls by the selected method at the selected frequency and reads matching files once they become available. The reader continually watches for new files matching the file path provided using the watch method.
When using watching the pipeline continues watching until there is manual intervention to finish the pipeline.
Note
Watching should not to be used with a Database Writer using the direct write option
When using the Watching option it is not possible to pair this with a Database Writer using direct write since direct write relies on a definitive finish point which is not guaranteed when using this option.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
v1 |
v2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Path |
Add one or more S3 URIs to read from an Amazons S3 Cloud Storage bucket |
|
✔ |
✔ |
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
v1 |
v2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Region |
The AWS region of the bucket to authenticate against |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Tenant |
The authentication tenant, if applicable. |
|
✔ |
❌ |
|
File Mode |
The file read mode. Setting the file mode to |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Offset |
A byte or character offset to start reading at. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunking |
Splits file into smaller batches. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Chunk Size |
File size of chunks when chunking is enabled. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Use Watching |
Watch for new S3 objects matching the given S3 URI(s). |
No |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Method |
Method used to watch for new files. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Frequency |
Frequency of timer polling. Only available if |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Use Authentication |
Enable Kubernetes secret authentication. |
|
✔ |
❌ |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret to authenticate with Google Cloud Storage. Only available if |
|
✔ |
❌ |
Amazon S3 Authentication
To access private buckets or files, a Kubernetes secret needs to be created that contains valid AWS credentials. This secret needs to be created in the same namespace as the kdb Insights Enterprise install. The name of that secret is then used in the Kubernetes Secret field when configuring the reader.
To create a Kubernetes secret containing AWS credentials:
Bash
kubectl create secret generic --from-file=credentials=<path/to/.aws/credentials> <secret-name>
Where <path/to/.aws/credentials> is the path to an AWS credentials file, and <secret-name> is the name of the Kubernetes secret to create.
Note that this only needs to be done once, and each subsequent usage of the Amazon S3 reader can re-use the same Kubernetes secret.
Note
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
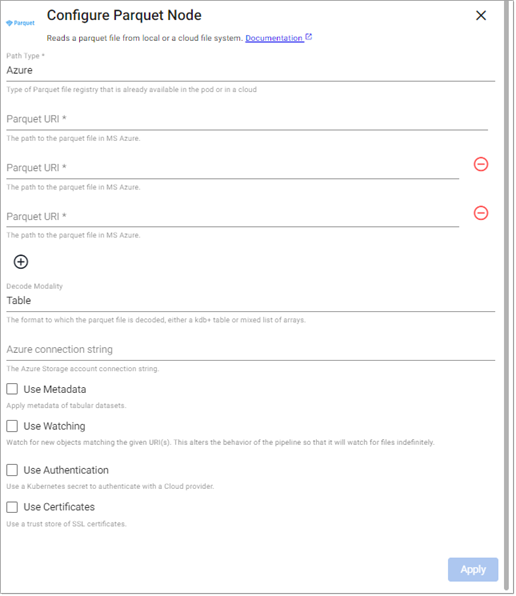
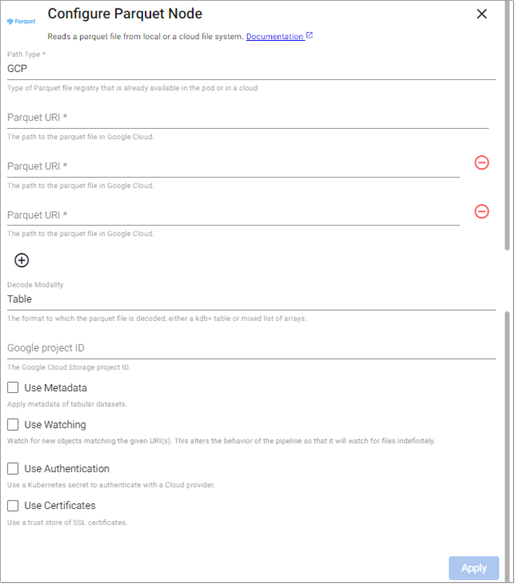
Parquet
This reads a parquet file.
Local Storage
Amazon S3
Azure
Google Cloud
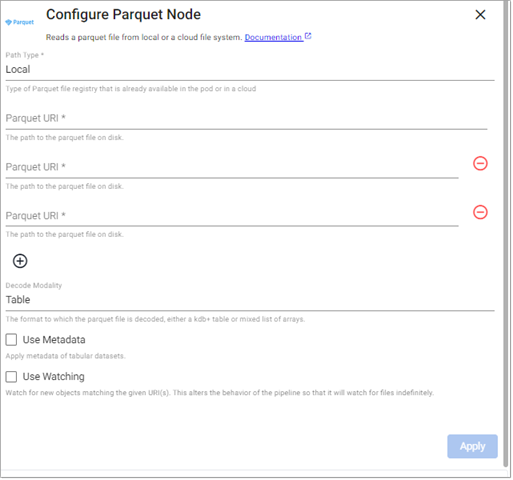
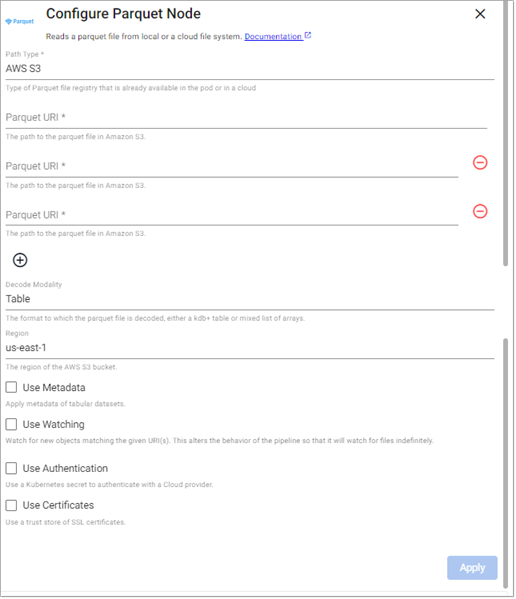
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Parquet
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Path Type |
Type of Parquet file registry in the cluster or in a cloud the file is read from, either |
|
|
Path |
Path to one or more parquet file(s) being read from disk or Amazon S3/MS Azure/Google Cloud. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Decode Modality |
Either |
|
|
Region |
The AWS region to authenticate against, if |
|
|
Azure Connection String |
The Azure Storage account connection string, if |
|
|
Google project ID |
The Google Cloud Storage project ID, if |
|
|
Use Watching |
Watch for new Cloud Storage objects matching the given path. Only available if |
No |
|
Use Authentication |
Enable Kubernetes secret authentication. |
No |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret to authenticate with a Cloud Storage. Only available if |
|
|
Use Certificates |
Use a trust store of SSL certificates. |
No |
|
Trust Store |
Location of default trust store of SSL certificates. Only available if |
|
|
Use Tenant |
Use tenant for Kurl authentication, if |
No |
|
Tenant |
The authentication tenant, if applicable. Only available if |
No |
Note
The reader may not handle parquet files which are larger then the total amount of memory or the size of the temporary Storage Directory. To handle such files, you can partition them into separate tabular datasets.
To configure authentication for each cloud provider, see the following:
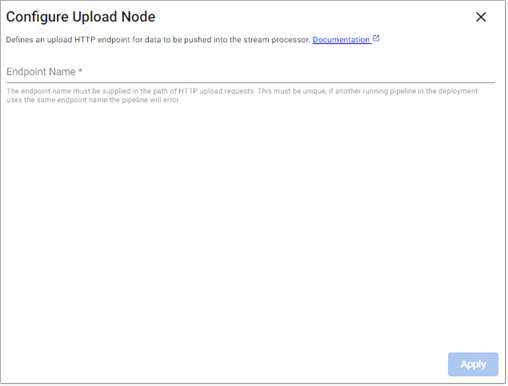
Upload
This reads data supplied through an HTTP endpoint.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: Upload
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Endpoint Name |
Unique name for this Upload node. This must be supplied in the path of HTTP upload requests. The fully qualified request path is displayed once this is entered. For example, |
Required |
Example
Once the pipeline is deployed you can upload files using HTTP by editing the template curl command:
Bash
curl -X POST "https://insights.kx.com/streamprocessor/upload/{Endpoint Name}?table=z&finish=true" \
--header "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--header "Authorization: Bearer $INSIGHTS_TOKEN" \
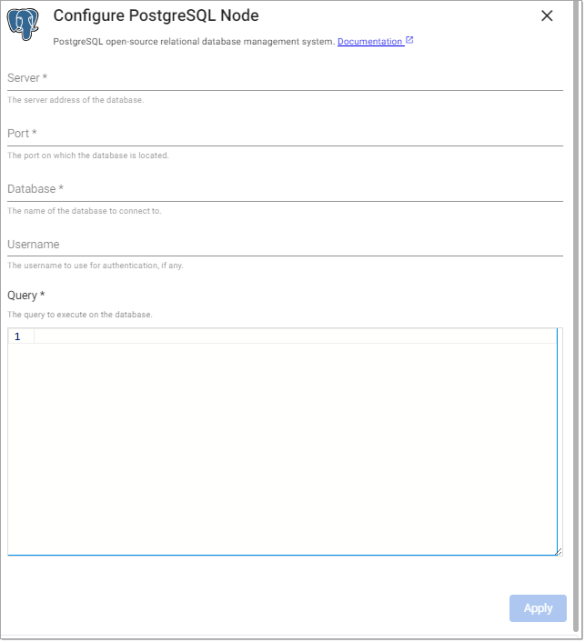
--data-binary "@my/file.csv"PostgreSQL
This executes a query on a PostgreSQL database.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: PostgreSQL
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Server |
The hostname of the database to issue a query against. |
|
|
Port |
The port to use for connecting to the database server. |
|
|
Database |
The name of the database to issue a query against in the target server. |
|
|
Query |
An SQL query to issue against the target database for pulling data into the pipeline. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Username |
The user account to use when establishing a connection to a PostgreSQL server. Note that if the username is provided, a password prompt appears during deploy time. |
|
|
Read Mode |
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of |
|
|
Period |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
|
|
Set Start Time |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
Unchecked |
|
Start Time |
The time the initial read is triggered. |
|
Note
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The is the package name if deployed as part of a package or the helm release name if deployed standalone.
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.
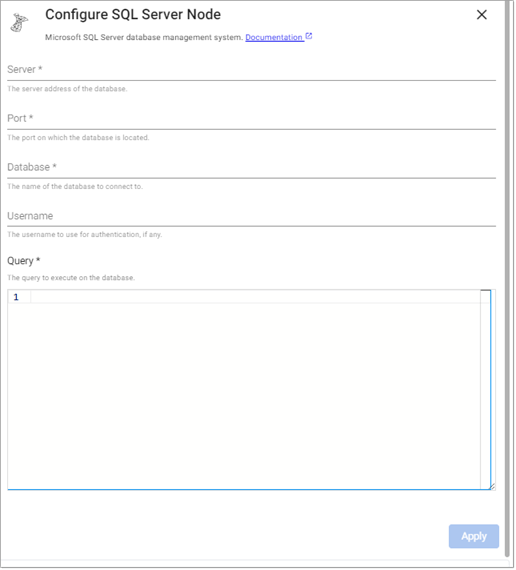
SQL Server
This executes a query on a SQL Server database.
Note
Refer to the following q and Python APIs for more details: SQL Server
Information
This reader is also available in the import wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Server |
The hostname of the database to issue a query against. |
|
|
Port |
The port to use for connecting to the database server. |
|
|
Database |
The name of the database to issue a query against in the target server. |
|
|
Query |
An SQL query to issue against the target database for pulling data into the pipeline. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Username |
The user account to use when establishing a connection to a SQL server. Note that if the username is provided, a password prompt appears during deploy time. |
|
|
Read Mode |
Configures how the node is triggered. This can be one of |
|
|
Period |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
|
|
Set Start Time |
This field, displayed when the Read Mode is set to |
Unchecked |
|
Start Time |
The time the initial read is triggered. |
|
Note
The Trigger URL is displayed when Read Mode is set to API or Timer. This specifies the Trigger URL for the selected operator in the pipeline. This field is not editable. The
Refer to Pull Trigger Read Options for more details.