Transform
This page explains how to set up transform operators, for kdb Insights Enterprisepipelines, using the Web Interface.
Transform operators enable data type and shape conversions without the need to write the transformation as code.
Tip
Both q and Python (if PyKX is enabled) interfaces can be used to build pipelines programmatically. See the q and Python APIs for details.
The pipeline builder uses a drag-and-drop interface to link together operations within a pipeline. For details on how to wire together a transformation, see the building a pipeline guide.
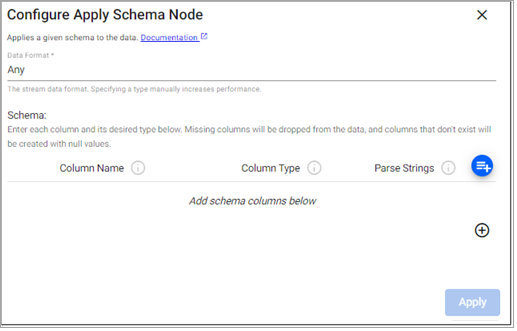
Apply Schema
This operator applies a table schema to data passing through the operator.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Note
This transform node is used by the Import Wizard to configure the schema for pipelines created using the wizard.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Data Format |
Indicates the format of the data within the stream if it is known. Selecting either |
|
|
Schema |
Enter a |
|
Schema Parameters:
|
name |
description |
|---|---|
|
Column Name |
Give the assigned column a name. |
|
Column Type |
Define the kdb+ type for the assigned column. |
|
Parse Strings |
Indicates if parsing of data type is required. Parsing of input data should be done for all time, timestamp, and string fields unless your input is IPC or RT. Defaults to |
Note
Schemas require a timestamp data column. In addition, the table should be partitioned and sorted (interval, historic and/or real-time) by this timestamp column. This can be configured as part of the essential properties of a schema.
Note
The parse option allows for string representations to be converted to typed values. For numeric values to
be parsed correctly, they must be provided in the expected format. String values in unexpected formats may
be processed incorrectly.
-
Strings representing bytes are expected as exactly two base 16 digits. For example,
"ff" -
Strings representing integers are expected to be decimal. For example
"255" -
Strings representing boolean values have a number of supported options. For example,
"t","1"More information on the available formats.
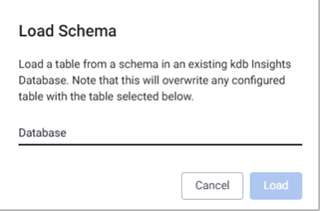
Load Schema
To load an existing schema, click the add schema button. 
This open the Load Schema dialog which allows you to select a schema from a list of schemas already entered in the system. Selecting a schema will copy all of the column and type definitions into the pipeline.

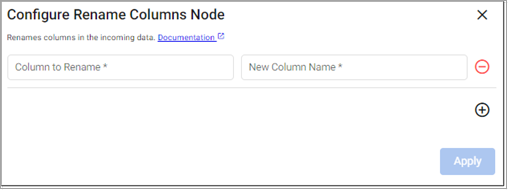
Rename Columns
This operator renames one or more columns in your data.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Renaming Scheme |
A dictionary that maps existing column names to their new desired names. |
|
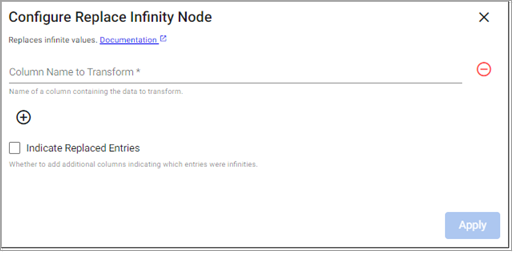
Replace Infinity
This operator replaces infinities in your data.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Source Columns |
A list of column names to act upon. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Indicate Replaced Entries |
Whether to create additional columns indicating which entries were replaced. |
No |
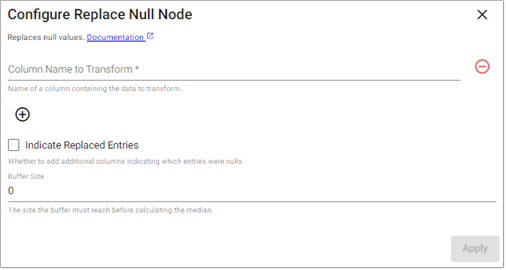
Replace Null
This operator replaces nulls in your data.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Source Columns |
A list of column names to act upon. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Buffer Size |
Number of data points that must amass before calculating the median. |
|
|
Indicate Replaced Entries |
Whether to create additional columns indicating which entries were replaced. |
Disabled |
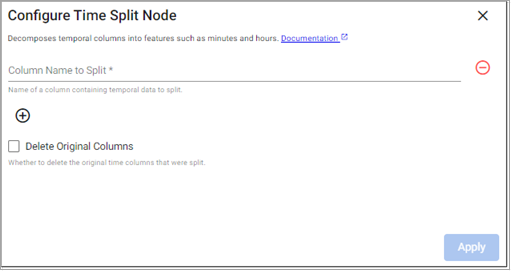
Time Split
This operator decomposes time data into subdivisions of hours, minutes, seconds.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Source Columns |
A list of column names to act upon. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Delete Original Columns |
Whether to delete the original source column(s). |
Disabled |