Writers
This page explains how to set up writer operators, for kdb Insights Enterprise pipelines, using the Web Interface.
Writers are a specialized type of operators that allow users to push data from a streaming pipeline to different external data sources, using the stream processor.
Tip
See APIs for more details
Both q and Python interfaces can be used to build pipelines programmatically. See the q and Python APIs for details.
The pipeline builder uses a drag-and-drop interface to link together operations within a pipeline. For details on how to build a pipeline, see the building a pipeline guide.
Amazon S3
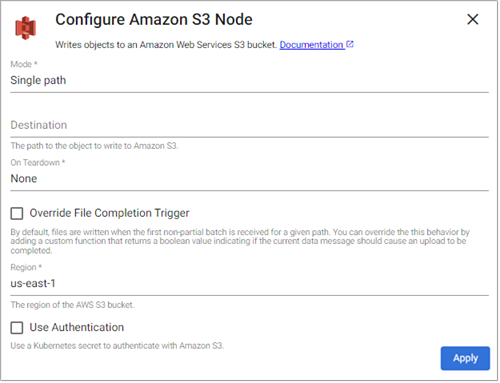
The Amazon S3 operator writes data to an object in an Amazon S3 bucket.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: Amazon S3
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Mode |
Indicates if this writer should write to a single file path or if it should use a function to derive a function path from the data in the stream. |
|
|
Destination |
If |
|
|
On Teardown |
Indicates the desired behavior for any pending data when the pipeline is torn down. The pipeline can perform no action ( |
None |
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Override File Completion Trigger |
When selected, an |
No |
|
Is Complete |
A function that accepts |
|
|
Region |
The AWS region of the bucket to authenticate against |
|
|
Use Authentication |
Enable Kubernetes secret authentication. |
No |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret to authenticate with Azure Cloud Storage. Only available if |
|
Amazon S3 Authentication
To access private buckets or files, a Kubernetes secret needs to be created that contains valid AWS credentials. This secret needs to be created in the same namespace as the kdb Insights Enterprise install. The name of that secret is then used in the Kubernetes Secret field when configuring the reader.
To create a Kubernetes secret containing AWS credentials:
Bash
kubectl create secret generic --from-file=credentials=<path/to/.aws/credentials> <secret-name> Where <path/to/.aws/credentials> is the path to an AWS credentials file, and <secret-name> is the name of the Kubernetes secret to create.
Note that this only needs to be done once, and each subsequent usage of the Amazon S3 reader can re-use the same Kubernetes secret.
Console
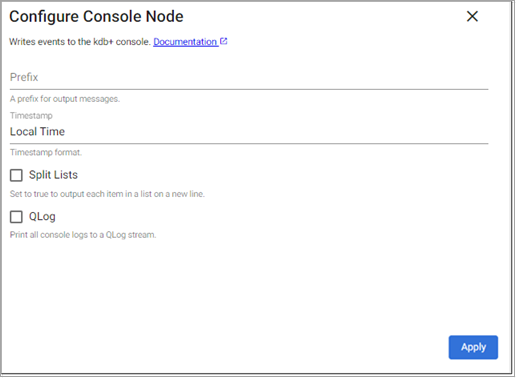
The Console operator writes to the console.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: Console
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Prefix |
A customized message prefix for data sent to the console. |
"" |
|
Timestamp |
Indicates what timezone should be used for timestamps, either |
|
|
Split Lists |
Indicates if each element of a list should be on its own line or if it can all be on a single line. |
No |
|
QLog |
Logs written by the console output are in raw text format. Check this option to wrap all output in QLog format. |
No |
kdb Insights Database
Use this operator to write data to a kdb Insights database. The operator properties, shown below, are described in the table that follows.
This writer is used by the Import Wizard to configure the writer for pipelines created using the wizard.
There are 2 versions of the kdb Insights Database writer operator.
-
Version 1: This is the original and default version.
-
Version 2: Enhances the ingest experience when Write Direct to HDB is enabled.
To change the operator version, click the Version drop-down to select either Version 1 or Version 2.
Note
Pipelines built using v1 of this operator retain this version unless you change it. If you change operator versions, the fields of the v2 screen are blank and the v2 fields have to be configured. The v1 current configuration is overwritten and the new configuration is applied when you click Apply. You are notified and asked to confirm this action.
Click the version tabs below to view the operator configuration options available for each version.
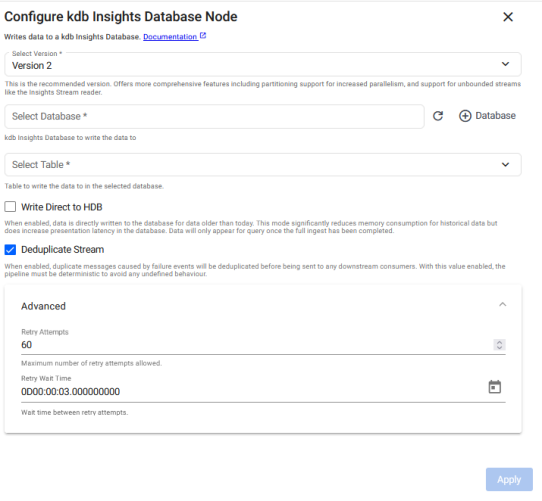
Version 2
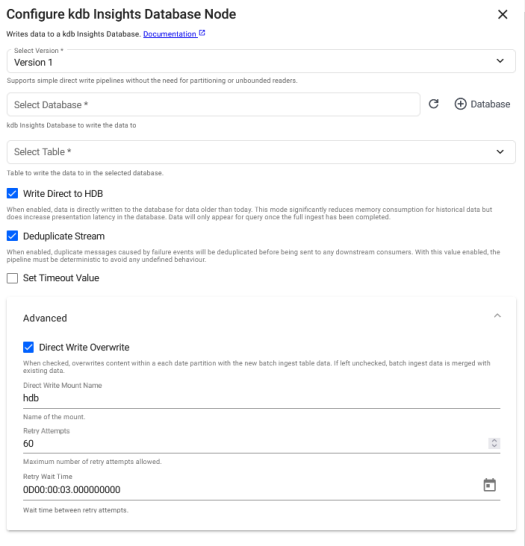
Version 1
Configuration options for the Version 2 kdb Insights Database node are described below.
Configuration options for the Version 1 kdb Insights Database node are described below.
|
name |
description |
default |
V1 |
V2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Database |
The name of the database to write data to. |
None |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Table |
The name of the table to insert data into. |
None |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Write Direct to HDB |
When enabled, data is directly written to the database. For large historical ingests, this option has significant memory savings. When this is checked, data is not available for query until the entire pipeline completes.
When a pipeline with this setting enabled is run, a status indicator shows the progress of the data ingest in the banner section of the database screen. The status of the ingest can also be seen on the Batch Ingest tab under Diagnostics. |
Unchecked |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Deduplicate Stream |
For deterministic streams, this option ensures that data that is duplicated during a failure event only arrives in the database once. Only uncheck this if your model can tolerate data that is duplicated but may not be exactly equivalent. This is only available if Write Direct to HDB is disabled.
In v2 of this operator, this field is not available if Write Direct to HDB is enabled. |
Enabled |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Set Timeout Value |
This controls whether to set a database connection timeout. |
Set Timeout Value |
✔ | ❌ |
|
Timeout Value |
The database connection timeout value. |
Timeout Value |
✔ | ❌ |
|
Direct Write Overwrite |
This is only displayed when Write Direct to HDB is enabled. When checked, this overwrites content within each data partition with the new batch ingest table data. When this is unchecked, batch ingest data is merged with existing data. |
Unchecked |
✔ |
✔ |
|
Direct Write Mount Name |
This is only displayed in the Advanced parameters when Write Direct to HDB is enabled. When using direct write, this name indicates the name of the mount to use writing to the database. This must match the database mount name used for the HDB tier. This value corresponds to |
|
✔ | ❌ |
|
Retry Attempts |
The maximum number of database connection attempts. |
|
✔ |
✔ |
|
Retry Wait Time |
The wait time between retry attempts. Click on the time picker to select the hours, minutes, and seconds. |
0D00:00:03.000000000
|
✔ |
✔ |
Required fields are marked with an asterisk *. Click + Database to create a new database.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: kdb Insights Database
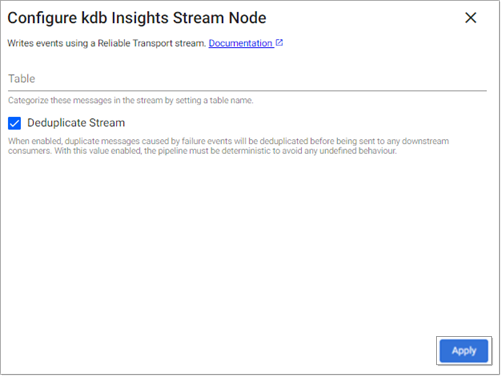
kdb Insights Stream
The kdb Insights Stream operator writes data using a kdb Insights Reliable Transport stream.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: kdb Insights Stream
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Table |
Wraps outbound data with the given table name as part of the message. Without this field, data is sent using the key name as the table name. Leave this blank for pipelines that both read and write from a stream. |
|
|
Deduplicate Stream |
For deterministic streams, this option ensures that data that is duplicated during a failure event only arrives in the database once. Only uncheck this if your model can tolerate data that is duplicated but may not be exactly equivalent. |
Yes |
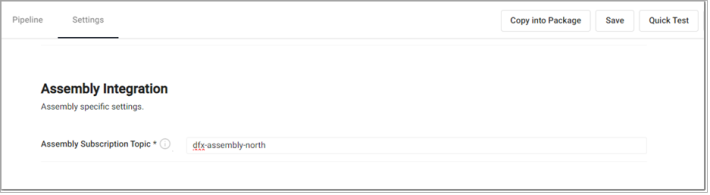
To write data to a stream, an assembly must be provided. This is done at pipeline deploy time. When you click the Deploy button and select the Assembly Integration tab. On this page, you need to set the assembly name and topic name.
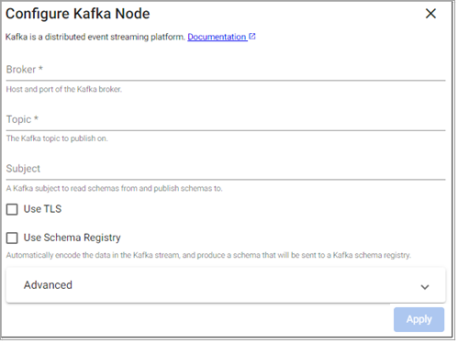
Kafka
The Kafka operator publishes data on a Kafka topic.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: Kafka
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Broker |
Location of the Kafka broker as host:port. If multiple brokers are available, they can be entered as a comma separated list. |
|
|
Topic |
The name of the Kafka topic to subscribe to. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Use TLS |
Enable TLS for encrypting the Kafka connection. When selected, certificate details must be provided with a Kubernetes TLS Secret |
No |
|
Kubernetes Secret |
The name of a Kubernetes secret that is already available in the cluster and contains your TLS certificates. Only available if Use TLS is selected. |
|
|
Certificate Password |
TLS certificate password, if required. Only available if Use TLS is selected. |
|
|
Use Schema Registry |
Use the schema registry to automatically decode data in a Kafka stream for JSON and Protocol Buffer payloads. When enabled, will automatically deserialize data based on the latest schema. |
No |
|
Registry |
Kafka Schema Registry URL. Only available if Use Schema Registry is selected. |
|
|
Auto Register |
Whether or not to generate and publish schemas automatically. When enabled, the Stream Processor updates the registry with a new schema if the shape of data changes. If false, the schema for this topic must already exist. |
No |
Advanced Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
|
The maximum number of retry attempts allowed. |
|
|
|
The amount of time to wait between retry attempts. |
|
Note
Allows more flexible options for security protocol configuration or changes to fetch intervals, as seen when subscribing to an Azure Event Hub Kafka connector.
See this guide for more details on setting up TLS Secrets
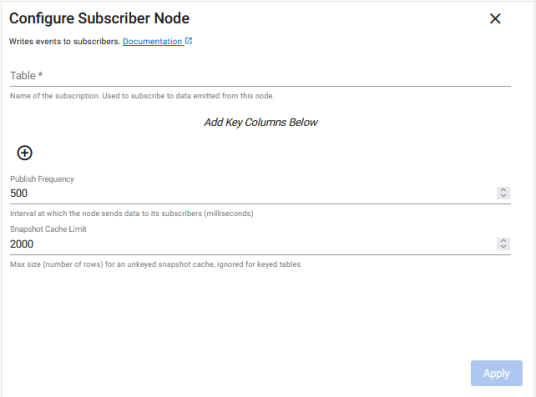
Subscriber
This node is used to publish data to websocket subscribers, such as kdb Insights Enterprise Views. It buffers data and publishes at a configurable frequency. Filters can be applied to focus on a specific subset of the data and optionally keys can be applied to see the last value by key. When subscribing to the stream, subscribers will receive an initial snapshot with the current state of the subscription and then receive periodic updates as the node publishes them.
When configuring the operator you must decide whether it is keyed or not.
-
Keyed: When configured with keyed columns, it stores and publishes the latest record for each unique key combination. For example, a subscriber wanting to see the latest stock price by symbol.
-
Unkeyed: When configured without any key columns, the node publishes every row it receives and store a configurable buffer size. This buffer is used for snapshots and stores a sliding window of the latest records received. For example, a subscriber to the last 100 trades for a symbol. Once the buffer size limit is reached, it drops older records to store new ones.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details: Subscriber
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Table |
Name of the subscription. Used to subscribe to data emitted from this operator. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Keyed Columns |
A list of keyed columns in the input data, for example |
|
|
Publish Frequency |
Interval at which the operator sends data to its subscribers (milliseconds) |
|
|
Snapshot Cache Limit |
Max size (number of rows) for an unkeyed snapshot cache. This is required when the node is configured as unkeyed. When you add keyed columns this field is not displayed. |
|
Process
The Process operator writes data to a kdb+ process.
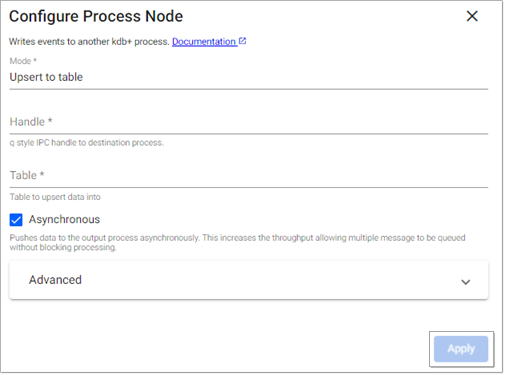
Note
See APIs for more details q and Python APIs: Process
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Mode |
Chose for data to either be added to a table in the remote process or to call a function. |
|
|
Handle |
An IPC handle to a destination process (ex. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Table |
When using |
|
|
Function |
When using |
|
|
Parameter |
When using |
|
|
Asynchronous |
Indicates if data should be sent to the remote process asynchronously. If unchecked, the pipeline will wait for the remote process to receive each batch of data before sending the next. Disabling this will add significant processing overhead but provide greater reliability. |
Yes |
Advanced Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Retry Attempts |
The maximum number of retry attempts allowed. |
|
|
Retry Wait Time |
The amount of time to wait between retry attempts. |
|
|
Queue Length |
The maximum async message queue length before flush. |
|
|
Queue Size |
The maximum number of bytes to buffer before flushing. |
|