Pipeline Settings
This page describes how to configure pipeline settings in the Web Interface.
When creating a pipeline, the Settings tab lets you configure resources, environment variables, and other tuning options. The following sections detail these settings.
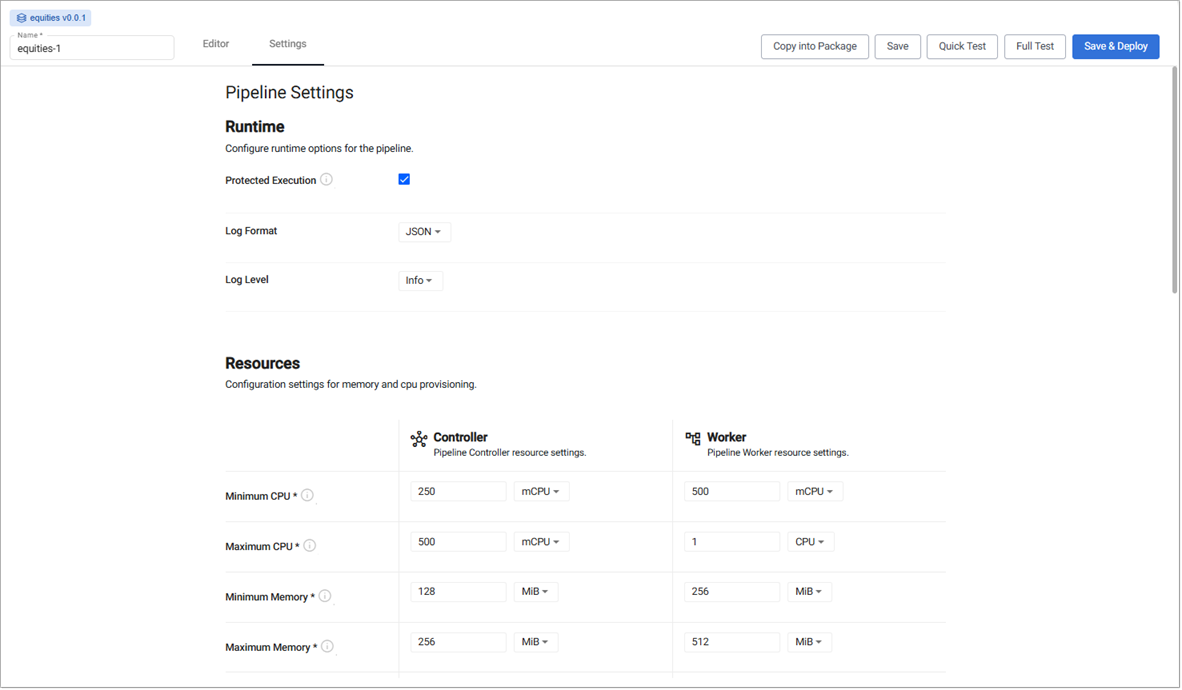
The screenshot above shows a partial view; scroll to see all settings.
Runtime
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enabled for greater granularity in error reporting. When enabled, operating performance may be impacted. |
|
|
Define debug reporting format; select between |
|
|
Select between |
Resources
Resources are the amount of computational resources that this pipeline is allowed to consume. When allocating resources, it is important to remember that only the worker is responsible for processing data. To increase throughput, increase resources on the worker. The controller resources only needs to be modified when a high degree of parallelism is used.
Controller
CPU
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Minimum amount of CPU for the controller; |
|
|
Maximum amount of CPU for the controller; must be <= |
Memory
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Minimum memory to allocate to the controller and always be available; >= |
|
|
Maximum memory to allocate to the controller; once reached it returns |
Worker
CPU
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Minimum amount of CPU for for the worker; |
|
|
Maximum amount of CPU for for the worker. |
Memory
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Minimum memory to allocate to the worker and always be available; >= |
|
|
Maximum memory to allocate to the worker; once reached it returns |
Config
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Define the minimum number of workers that can be created to run the pipeline; >= |
|
|
Define the maximum number of workers that can be created to run the pipeline; <= |
|
|
Maximum number of worker threads; value between |
Metrics
Customize or disable pipeline metrics.
Record counting
Pipeline record counting allows pipelines to calculate an average input and output data rate, which is a good indication of how much data the pipeline is ingesting and outputting. Disabling record counting increases pipeline performance by a small amount.
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enable record counting for all readers and writers, allowing input and output data rates to be calculated. |
|
|
Disable record counting. This increases performance but doesn't allow input and output data rates to be calculated. |
Persistence
Controller
Kubernetes persistence configuration.
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enabled by default, click to disable. |
|
|
Kubernetes storage class name; e.g. |
|
|
Size volume allocated to each controller; defaults to |
|
|
Check frequency in milliseconds, defaults to |
Note
Ensure Storage Class is set to a valid class. This is defined in the cluster and may be different across cloud providers i.e. GCP: standard, AWS: gp2, Azure: default. This information can be retrieved by running:
shell
kubectl get storageclass
Worker
Kubernetes persistence configuration.
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enabled by default, click to disable. |
|
|
Kubernetes storage class name; e.g. |
|
|
Size volume allocated to each Worker; defaults to |
|
|
Check frequency in milliseconds, defaults to |
Kubernetes
|
item |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Add a label and value to created resources. This is a Kubernetes label and can be used to identify resources associated with this pipeline. |
|
|
Add Kubernetes secret reference name; for example, |
Environment Variables
Environment variables can be used as overrides to customize the behavior of the Stream Processor. See the list of environment variables for available options.
Advanced
|
Field |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
The number of pipeline replicas to deploy. Default value of |
|
|
A registry URL that points to a custom Stream Processor worker image. This can be used for extending the core set of functionality of the Stream Processor with custom code or libraries. |
|
|
A registry URL that points to a custom Stream Processor controller image. |
|
|
This enables unsafe mode, which disables determinism and may lead to duplicate or lost data in failover scenarios. The options are:
|
Test timeout
This setting defines the maximum amount of time a test is allowed to run before it automatically times out. It ensures that tests do not hang indefinitely if expected data does not arrive in time.
A timeout is especially useful when the timing of incoming data is unpredictable, such as when the pipeline involves multiple readers. Setting a timeout improves the overall testing experience and removes the need to either use a full deployment for testing or stub out data readers with a callback function.
This timeout applies when running both quick and full tests, with an additional 20-second startup buffer for full tests.
|
setting |
description |
|---|---|
|
|
Enter the timeout duration in seconds. The default value is 10 seconds |