Windows
This page explains how to set up windows operators, for kdb Insights Enterprisepipelines, using the Web Interface.
Windows allow data to be grouped into buckets so they the data can be aggregated over temporal or logical groups. Windows are typically created using temporal characteristics within the data, but they can also use processing time or record count to group data.
Tip
Both q and Python (PyKX is enabled) interfaces can be used to build pipelines programmatically. See the q and Python APIs for details.
The pipeline builder uses a drag-and-drop interface to link together operations within a pipeline. For details on how to wire together a transformation, see the building a pipeline guide.
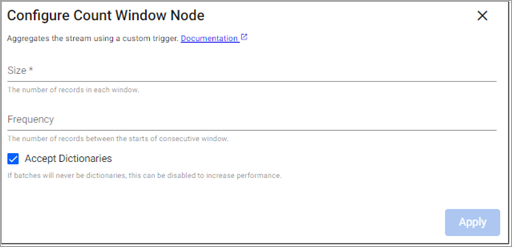
Count Window
This operator splits the stream into equally sized windows.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Size |
The number of records to include in each window. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Frequency |
The number of records between the starts of consecutive windows. If the size of the window is larger than the frequency, windows overlap. If they are the same size, windows have no overlap. If the frequency is larger than the size, there are gaps in the output. |
Defaults to the size of the window |
|
Accept Dictionaries |
Whether to accept dictionary batches. Can be set to false to increase performance if batches are never dictionaries. |
Enabled |
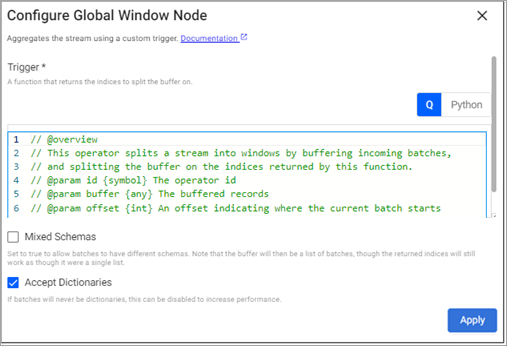
Global Window
This operator aggregates the stream using a custom trigger.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Trigger |
A function that returns the indices to split the stream into. Indices that are returned are emitted, other records are buffered. See below for details on the trigger function. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Mixed Schemas |
Set to true if batches are tables with different schemas. Buffering tables with different schemas may significantly impact performance. |
Disabled |
|
Accept Dictionaries |
Whether to accept dictionary batches. Can be set to false to increase performance if batches are never dictionaries. |
Enabled |
Trigger Function:
The trigger function is passed the following parameters
-
id- The operator id. -
buffer- Any buffered records from previous batches. -
offset- An offset in the stream where the current batch starts. -
md- The current batch's metadata -
data- The current batches' data.
As batches are ingested, the trigger function is applied to each batch, and data is buffered. However, the buffering behavior depends on the output of the trigger function:
-
If the trigger function returns an empty list or generic null, the incoming batch is buffered and nothing is emitted.
-
If the trigger function returns numbers, the buffer is split on those indices, with each index being the start of a new window.
Note
Last data batch
The last list remains in the buffer. This last list can be emitted by returning the count of the buffer as the last index. To map indices in the current batch to indices in the buffer, add the offset parameter to the indices.
The buffered records cannot be modified from the trigger function.
Batches with mixed schemas are only supported when using the mixed schemas option.
Note
Caveat when using mixed schemas
When this is set, the buffer passed to the trigger is a list of batches, rather than a single table. The indices returned by the trigger function still works as though the buffer were a single list.
On teardown, any records left in the buffer is emitted as a single batch.
This pipeline emits a window whenever the high water mark is exceeded.
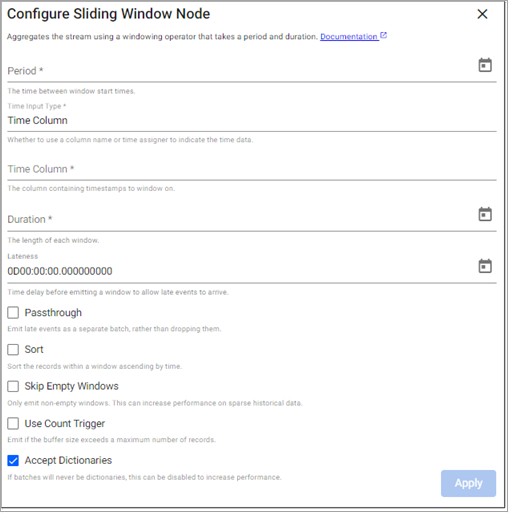
Sliding Window
This operator aggregates the stream into potentially overlapping windows based on event time.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Period |
How frequently the window is to emit data. |
|
|
Time Input Type |
Whether to use a time column or time assigner to indicate temporal data. |
|
|
Time Column |
The name of the column containing the temporal data of the records. Required when Time Input Type is set to |
|
|
Time Assigner |
A function that extracts temporal data from the batch of data being processed. Required when Time Input Type is set to |
|
|
Duration |
The length of each window. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Lateness |
Data that is destined for a particular window may arrive after the window is set to emit. To allow for data to still be collecting in the desired window, add a lateness value. Windows wait this additional bit of time before emitting for any data that was intended for the current window. |
0 |
|
Passthrough |
By default, any late data that is received after a window has been emitted is dropped. Check this box to keep late data and pass it through the window immediately. |
Disabled |
|
Sort |
If checked, sorts the window in ascending temporal order. |
Disabled |
|
Skip Empty Windows |
Check to ignore windows that have no data for the specified time boundaries. |
Disabled |
|
Use Count Trigger |
Check this value to set a maximum number of records for a window before emitting. |
Disabled |
|
Count Trigger |
When Use Count Trigger is selected, this field is the maximum number of records to buffer before emitting automatically. |
Infinity |
|
Accept Dictionaries |
Whether to accept dictionary batches. Can be set to false to increase performance if batches are never dictionaries. |
Yes |
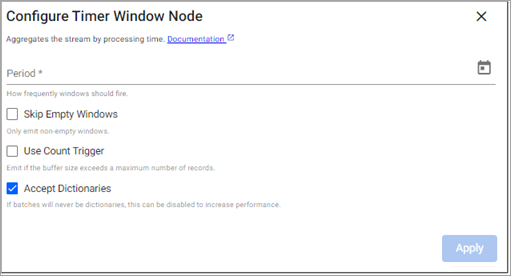
Timer Window
This operator aggregates the stream by processing time.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Period |
How frequently the window is to emit data. |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Skip Empty Windows |
Check to ignore windows that have no data for the specified time boundaries. |
Disabled |
|
Use Count Trigger |
Check this value to set a maximum number of records for a window before emitting. |
Disabled |
|
Count Trigger |
When Use Count Trigger is selected, this field is the maximum number of records to buffer before emitting automatically. |
Infinity |
|
Accept Dictionaries |
Whether to accept dictionary batches. Can be set to false to increase performance if batches are never dictionaries. |
Yes |
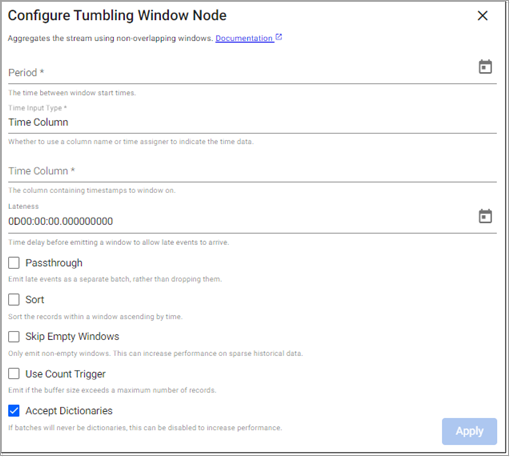
Tumbling Window
This operator aggregates the stream into non=overlapping windows based on event time.
Note
See q and Python APIs for more details.
Required Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Period |
How frequently the window is to emit data. |
|
|
Time Input Type |
Whether to use a time column or time assigner to indicate temporal data. |
|
|
Time Column |
The name of the column containing the temporal data of the records. Required when Time Input Type is set to |
|
|
Time Assigner |
A function that extracts temporal data from the batch of data being processed. Required when |
|
Optional Parameters:
|
name |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
Lateness |
Data that is destined for a particular window may arrive after the window is set to emit. To allow for data to still be collecting in the desired window, add a lateness value. Windows wait this additional bit of time before emitting for any data that was intended for the current window. |
0 |
|
Passthrough |
By default, any late data that is received after a window has been emitted is dropped. Check this box to keep late data and pass it through the window immediately. |
Disabled |
|
Sort |
If checked, sorts the window in ascending temporal order. |
Disabled |
|
Skip Empty Windows |
Check to ignore windows that have no data for the specified time boundaries. |
Disabled |
|
Use Count Trigger |
Check this value to set a maximum number of records for a window before emitting. |
Disabled |
|
Count Trigger |
When Use Count Trigger is selected, this field is the maximum number of records to buffer before emitting automatically. |
Infinity |
|
Accept Dictionaries |
Whether to accept dictionary batches. Can be set to false to increase performance if batches are never dictionaries. |
Enabled |