Persist Data to Object Storage
This page provides details on how to persist data to object storage.
kdb Insights Enterprise can persist data to object storage for durable, long-term data storage. Persisting to object storage has major cost saving implications, and is worth considering for older data sets.
Note
Immutable data
Data in object storage cannot be modified. It is best suited for data that is meant for long term storage. If the data is modified/deleted externally, restart any HDB pods, and drop cache.
Tip
Object storage tiers vs mounting an object storage database
An object storage tier is a read-write location and is configured differently than a read-only database. See querying object storage for an example of how to query an existing object storage database.
An object storage tier has to be the final tier in your storage configuration.
Authentication
You need to provide authentication details to access your private buckets. Object storage tiers can be configured using environment variables for routing details and for authentication. Authentication can also be configured using service accounts.
Note
Authentication
For more information on service accounts see automatic registration and environment variables.
AWS
Azure
GCP
|
variable |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
| AWS_REGION |
AWS S3 buckets can be tied to a specific region or set of regions. This value indicates what regional endpoint to use to read and write data from the bucket. |
|
|
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID |
AWS account access key ID. |
|
|
AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY |
AWS account secert access key. |
|
See this guide on service accounts in EKS on how to use an IAM role for authorization.
|
variable |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT |
The storage account name to use for routing Azure blob storage requests. |
|
|
AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY |
A shared key for the blob storage container to write data to. |
|
See this guide on service accounts in AKS to use an IAM role for authorization.
|
variable |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|
|
GCLOUD_PROJECT_ID |
Name of the Google Cloud project ID to use when interfacing with cloud storage. |
|
See this guide on service accounts in GKE on how to use an IAM role for authorization.
Set environment variables
Package
Web Interface
In a package, environment variables need to be set within the deployment config.
deployment_config/deployment_config.yaml:
YAML
env:
- name: AWS_REGION
value: us-east-2
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: aws-access-secret
key: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: aws-access-secret
key: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
In the kdb Insights EnterpriseWeb Interface, environment variables need to be set for both the query settings and writedown settings of a database's configuration.
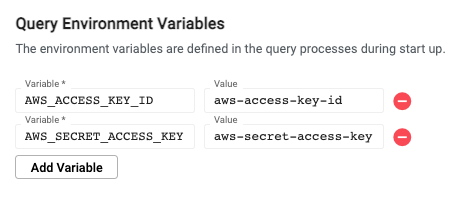
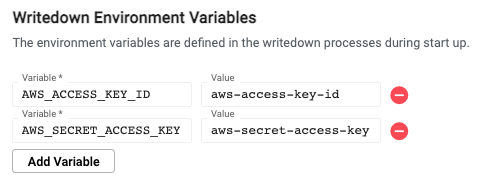
Performance considerations
Consider the layout of your table before uploading it to object storage. Neglecting to apply attributes, as well as not sorting symbols or partitioning by date can result in any query becoming a linear scan that pulls back the whole data set.
Attributes and table layouts are specified in the tables directory of the package.
Deployment
To persist data to cloud storage, you must deploy a package with an HDB tier that has a storage key. This setting creates a segmented database where the HDB loads on-disk and cloud storage data together seamlessly.
Data in object storage is immutable, and cannot be refactored after it has been written. For this reason, date-based partitions bound for object storage can only be written down once per day.
For example, this Storage Manager tier configuration:
-
Stores data in memory for 10 minutes
-
Keeps the last 2 days of data on disk
-
Migrates data older than 2 days to object storage
YAML
sm:
tiers:
- name: streaming
mount: rdb
- name: interval
mount: idb
schedule:
freq: 00:10:00
- name: ondisk
mount: hdb
schedule:
freq: 1D00:00:00
snap: 01:35:00
retain:
time: 2 days
- name: s3
mount: hdb
store: s3://examplebucket/db
Warning
Mounts
You may see other kdb Insights Enterprise examples referring to object type mounts. Those mounts are for reading from existing cloud storage.
For writing your own database to storage, no object mounts are involved, only HDB tier settings to make your HDB a segmented database.
For a guide on reading from an existing object storage database see querying object storage
Example using explicit credentials
This example assumes your data is published into a topic called south.
AWS
Azure
The name of the example bucket is s3://examplebucket, and we want to save our database to a root folder called db. Our example uses the AWS_REGION: us-east-2. Stream processor and table schema sections have been omitted.
First create a new secret with your AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY.
bash
kubectl create secret generic aws-access-secret\
--from-literal=AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=${MY_KEY}\
--from-literal=AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=${MY_SECRET}
Now create your package, setting sm.tiers to write to an S3 store, and environment variables for storage.
deployment_config/deployment_config.yaml:
YAML
env:
- name: AWS_REGION
value: us-east-2
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: aws-access-secret
key: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: aws-access-secret
key: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
databases/XXX-db/shards/XXX-db-shard.yaml:
YAML
mounts:
rdb:
type: stream
baseURI: none
partition: none
dependency:
- idb
idb:
type: local
baseURI: file:///data/db/idb
partition: ordinal
hdb:
type: local
baseURI: file:///data/db/hdb
partition: date
dependency:
- idb
sm:
source: south
tiers:
- name: streaming
mount: rdb
- name: interval
mount: idb
schedule:
freq: 00:10:00
- name: ondisk
mount: hdb
schedule:
freq: 1D00:00:00
snap: 01:35:00
retain:
time: 2 Days
- name: s3
mount: hdb
store: s3://examplebucket/db
daps:
instances:
idb:
mountName: idb
hdb:
mountName: hdb
rdb:
tableLoad: empty
mountName: rdb
source: south
The name of the example storage container is ms://mycontainer, and we want to save our database to a folder within the container called db. Our example uses the AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT: iamanexample. This means the database is written to a folder called db, inside the container mycontainer for the storage account iamanexample. Stream processor and table schema sections have been omitted.
First create a new secret with your AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY.
bash
kubectl create secret generic azure-storage-secret --from-literal=AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY=${MY_KEY}
Next, create your package, setting sm.tiers to write to an Azure store container, and environment variables for storage.
deployment_config/deployment_config.yaml:
YAML
env:
- name: AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT
value: mystorageaccount
- name: AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: azure-storage-secret
key: AZURE_STORAGE_SHARED_KEY
databases/XXX-db/shards/XXX-db-shard.yaml:
YAML
mounts:
rdb:
type: stream
baseURI: none
partition: none
dependency:
- idb
idb:
type: local
baseURI: file:///data/db/idb
partition: ordinal
hdb:
type: local
baseURI: file:///data/db/hdb
partition: date
dependency:
- idb
sm:
source: south
tiers:
- name: streaming
mount: rdb
- name: interval
mount: idb
schedule:
freq: 00:10:00
- name: ondisk
mount: hdb
schedule:
freq: 1D00:00:00
snap: 01:35:00
retain:
time: 2 Days
- name: s3
mount: hdb
store: ms://mycontainer/db
daps:
instances:
idb:
mountName: idb
hdb:
mountName: hdb
rdb:
tableLoad: empty
mountName: rdb
source: south
Apply the package using the kdb Insights CLI:
sh
kxi package deploy object-tier