Query Resilience
This page explains query resilience in kdb Insights Enterpriseoutlines the recommended practices for establishing redundant connections across components, describes configuration methods, and provides guidance on using ordinals.
There are four process types in the query path: Gateway (GW), Resource Coordinator (RC), Data Access Process (DAP), and Aggregator (Agg). Each process can be configured with multiple replicas for resiliency.
Process connections are as follows.
-
GWs connect to multiple RCs. Each GW distributes requests round-robin across all known RCs.
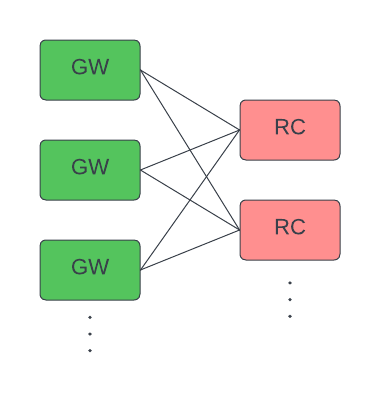
-
DAPs and Aggs connect to exactly one RC each. Hence, every RC owns its set of DAPs/Aggs.
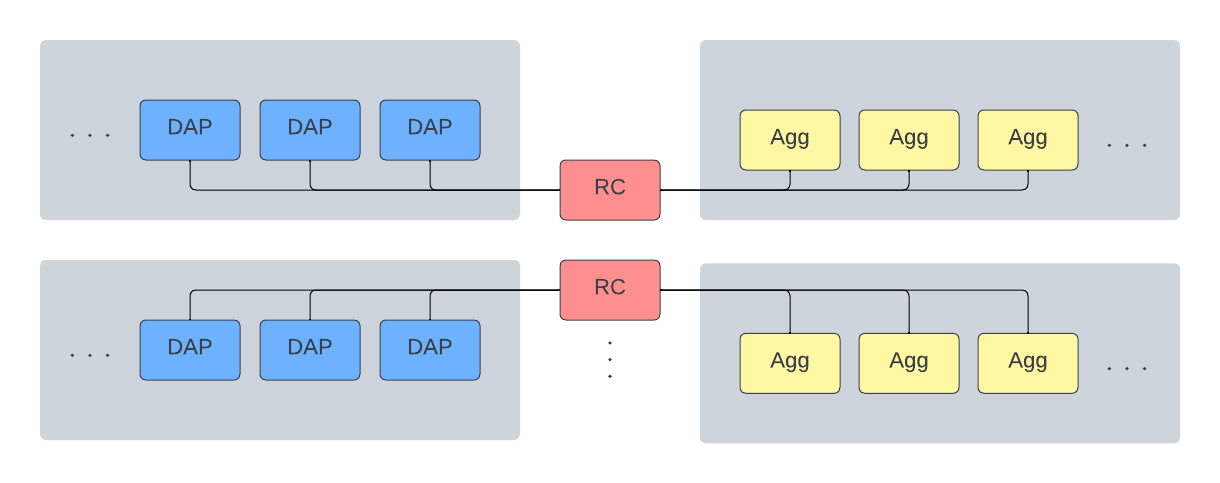
-
RCs can connect to each other.
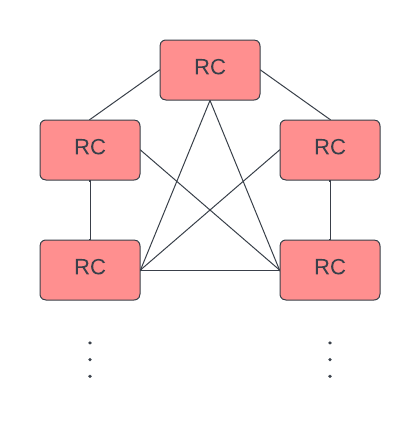
In general, it is best practice to allocate multiple of each resource at each connection point. That is:
-
Allocate multiple RCs, so that if one dies, the GWs can distribute to the remaining ones. If no RCs remain, requests return the following error:
"No Resource Coordinator connections are available and ready for service"
Refer to Troubleshooting for more details.
-
Allocate multiple DAPs (of each type RDB/IDB/HDB) for each label set to each RC. Multiple DAPs increase query throughput as RCs can distribute queries to several DAPs in parallel. If a DAP dies, the RC continues to distribute to the remaining ones. If no DAPs for a particular tier/label set are available, requests queue up in the RCs. Refer to Queueing for details.
-
Allocate multiple Aggs to each RC. Multiple Aggs increase query throughput as RCs can allocate queries across several Aggs. If an Agg dies, the RC allocates to the remaining ones. If no Aggs remain for a particular RC, requests received by this RC return a
"No aggregator available"error. Refer to Troubleshooting for more details.
Configuration
Learn how to configure:
kdb Insights
Using kdb Insights offers the greatest degree of flexibility around process connection at the cost of extra configuration. All processes connect to the RCs. The details for how to configure each process type are described below.
Gateway
You can configure the Gateway to connect to the RC(s) in one of three ways. They are listed below in decreasing order of decreasing precedence.
-
Environment variable
The simplest configuration method is to explicitly define the RC address(es) using the
KXI_SG_RC_ADDRenvironment variable in the GW container. This variable supports one or more RC addresses.bash
CopyKXI_SG_RC_ADDR="<rc_host1>:<rc_port1>,<rc_host2>:<rc_port2>"Note that this method restricts the GW to connect to a single RC.
-
Kubernetes control plane.
If using Kubernetes, configure the GW to connect to RCs using Kubernetes labels. For this method, the GW pod requires Kubernetes RBAC permissions for the "get", "watch", and "list" verbs of the "pods" resource.
Note that GWs connect to all RCs it is configured to discover. The GWs round-robin between them on each request. Moreover, the GW can target a specific set of RCs using scope.
Below is an example configuration.
YAML
Copy# GW pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: insights-gateway
spec:
serviceAccountName: insights-serviceAccount
containers:
# GW container
- ...
env:
# The following environment variables control what RCs the GW will find. Shown here are the default values; they
# are used if the corresponding environment is not defined. These can be overwritten to allow for fine-tuned
# controlled over GW-RC connections.
# - RC_LABEL_SELECTOR Label selector to identify/filter RC pods (`kubectl get pods -l '...').
# - RC_CONTAINER_NAME Name of the RC's container within the RC pod.
- name: KXI_RC_LABEL_SELECTOR
value: app.kubernetes.io/name=resource-coordinator
- name: KXI_RC_CONTAINER_NAME
value: resource-coordinator
---
# GW service account.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: insights-gateway-service-account
---
# RBAC role.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: insights-gateway-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
---
# RoleBinding RBAC role to GW's ServiceAccount.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: insights-gateway-role-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: insights-gateway-service-account
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: insights-gateway-role
apiGroup: ""The GW(s) connect to all RCs with the corresponding metadata labels:
YAML
Copykind: Pod
metadata:
name: insights-resource-coordinator
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: "resource-coordinator" # Must match GW's KXI_RC_LABEL_SELECTOR
spec:
containers:
- resource-coordinator: # Must match GW's KXI_RC_CONTAINER_NAME
ports:
- ...
containerPort: 5050 # Must set a port for the GW to connect to
protocol: TCP
Data access process
DAPs connect to their respective RCs in one of three ways. They are listed here in order of decreasing precedence.
-
Environment variable
Configure a DAP to explicitly connect to a particular RC by defining the RC address in the
KXI_SG_RC_ADDRenvironment variable.bash
CopyKXI_SG_RC_ADDR="<rc_host>:<rc_port>" -
Kubernetes discovery
If using Kubernetes, configure the DAPs to connect to RCs using Kubernetes labels. For this method, the DAP pods require Kubernetes RBAC permissions for the "get", and "list" verbs of the "pods" resource.
Refer to Kubernetes configuration for an example configuration.
Note that, while DAPs may discover multiple RCs (all those matching the configured label selector), each DAP connects to one RC using ordinals.
Aggregator
Aggs connect to to their respective RCs in one of below methods. They are listed here in order of decreasing precedence.
-
Environment variable
Configure an Agg to explicitly connect to a particular RC by defining the RC address in the
KXI_SG_RC_ADDRenvironment variable.bash
CopyKXI_SG_RC_ADDR="<rc_host>:<rc_port>" -
Kubernetes discovery
If using Kubernetes, configure the Aggs to connect to RCs using Kubernetes labels. For this method, the Agg pods require Kubernetes RBAC permissions for the "get", and "list" verbs of the "pods" resource.
Refer to Kubernetes q configuration for an example configuration.
Note that, while Aggs may discover multiple RCs (all those matching the configured label selector), each Agg connects to one RC using ordinals.
Resource coordinator
RCs connect to each other so they can enlist each other for help when the RC receiving the request does not contain the required DAPs to be able to complete the request on its own, Refer to Routing for details. RCs can only connect to each other using Kubernetes labels. The RC pods require Kubernetes RBAC permissions for the "get", and "list" verbs of the "pods" resource.
Refer to Kubernetes q configuration for an example configuration.
Note that global RCs connect to all RCs, and dedicated RCs connect only to other RCs within their respective packages. Refer to dedicated/global RCs for more information.
kdb Insights Enterprise
If you use kdb Insights Enterprise, no extra configuration is needed. DAP-RC and Agg-RC connection is done by ordinal.
Kubernetes q configuration
The following is an example configuration for Kubernetes-based discovery for q containers (DAP, RC, Agg).
YAML
# Connecting pod.
# Connecting pod.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: connecting-pod
spec:
serviceAccountName: insights-serviceAccount
containers:
# Connecting container.
- ...
env:
# Enable Kubernetes discovery.
- name: KXI_DISC_MODE
value: kubernetes
# The following environment variables control what RCs the connecting container will find. Shown here are the
# default values; they are used if the corresponding environment is not defined. These can be overwritten to allow
# for fine-tuned controlled over RC connections.
# - RC_LABEL_SELECTOR Label selector to identify/filter RC pods (`kubectl get pods -l '...').
# - RC_CONTAINER_NAME Name of the RC's container within the RC pod.
- name: KXI_RC_LABEL_SELECTOR
value: app.kubernetes.io/name=resource-coordinator
- name: KXI_RC_CONTAINER_NAME
value: resource-coordinator
---
# Service account.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: insights-service-account
---
# RBAC role.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: insights-role
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
---
# RoleBinding RBAC role to GW's ServiceAccount.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: insights-role-binding
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: insights-service-account
apiGroup: ""
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: insights-role
apiGroup: ""
The Pod/container above discovers all RCs configured as shown below.
YAML
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: resource-coordinator
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: "resource-coordinator" # Must match connecting pod's KXI_RC_LABEL_SELECTOR
spec:
containers:
- resource-coordinator: # Must match connecting pod's KXI_RC_CONTAINER_NAME
ports:
- ...
containerPort: 5050 # Must set a port
protocol: TCP
RCs connect to all discovered RCs, whereas DAPs and Aggs connect to one of the discovered RCs using ordinals.
Ordinal connection
If you use Kubernetes-based discovery to connect to RCs, DAPs and Aggs, use ordinals. A process's ordinal is the number following the last "-" or "_" in the process's host name. If a process's host name has no number following the last "-" or "_", then its ordinal is 0. For example:
|
host name |
ordinal |
|---|---|
|
|
3 |
|
|
11 |
|
|
0 |
It is important to use properly numbered RC, DAP, and Agg replicas with sequential ordinals. Use Kubernetes StatefulSets or Docker compose replicas to do this.
In kdb Insights, in order for this method to work, RCs MUST set the following the KXI_RC_STS_SIZE environment variable to the total number of RCs.
bash
KXI_RC_STS_SIZE=<total_number_of_RCs>
In kdb Insights Enterprise, this environment variable is automatically set.
A DAP or Agg with ordinal n connects to the (unique) RC whose ordinal is congruent to n modulo KXI_RC_STS_SIZE. For example, in a system with 6 DAPs and KXI_RC_STS_SIZE=3:
|
DAP |
RC |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note
-
You must have at least as many DAPs and Aggs as RCs so that each RC has at least one DAP and one Agg.
-
We recommend that you have a number of DAPs and Aggs equal to a multiple of the number of RCs so that each RC has equal query throughput capacity.
-
We recommend using ordinal-based connections as described above (i.e. letting DAPs and Aggs determine the correct RC via modulo arithmic). However, for specialized setups, it may be desirable to override an individual pod's ordinal. This can be achieved using the
KXI_ORDINALenvironment variable. E.g.KXI_ORDINAL="1"sets the pod's ordinal to1regardless of the pod's actual ordinal in the stateful set.