Access Management
This page provides details on how access management is implemented in kdb Insights Enterprise using Keycloak..
The kdb Insights Enterprise utilizes Keycloak to offer a full range of authentication and authorization services. Full documentation on these topics is available here.
There are a number of available configurations within the Keycloak service. Below is an install values file extract with some sample settings. The following sections explain these settings.
YAML
global:
keycloak:
guiClientSecret: "gui-client-secret"
operatorClientSecret: "kxi-operator-client-secret"
keycloak:
auth:
existingSecret: kxi-keycloak
postgresql:
auth:
existingSecret: kxi-postgresql
importUsers: false
initUser:
enabled: false
name: "demoinsights"
auth: "<redacted>"
initClient:
enabled: false
clientId: "test-publisher"
clientSecret: "<redacted>"
resetPasswordAllowed: true
smtpServer:
host: smtp.host.net
from: admin@host.com
user: apikey
password: <redacted>
passwordPolicy:
enabled: true
policy:
passwordHistory: 24
length: 14
upperCase: 1
lowerCase: 1
specialChars: 1
digits: 1
forceExpiredPasswordChange: 90
text: |
<p>Password policy:</p>
<ul>
<li>At least one uppercase letter</li>
<li>At least one lowercase letter</li>
<li>At least one symbol</li>
<li>At least one number</li>
<li>Minimum length of 14 or greater</li>
<li>Not one of the previous 24 passwords</li>
</ul>
Internal clients
The global.keycloak values relate to internal clients created by the install process.
These clients allow components to communicate with the Keycloak service for authentication.
The values can be set explicitly as part of the install or are randomly generated
by the CLI installer.
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
string |
|
"" |
|
|
string |
|
"" |
Warning
When you install the application for the first time, these are persisted in your values file and your CLI config file. These must be re-used across subsequent upgrades.
Keycloak credentials
The values in the table below are set by the CLI at install/setup time. It creates Kubernetes secrets containing Keycloak credentials and these values are the secret names.
|
variable |
type |
value |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
string |
|
"" |
|
|
string |
|
"" |
Import users
importUsers allows the system administrator to set whether the initUser is imported on install.
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
bool |
|
|
Note
User import
By default the user import is disabled. As part of the CLI install, it is explicitly enabled, however for upgrades or non-CLI installs, the user realm is not imported. Flipping this value to true triggers the import.
Initial user
The keycloak.initUser is used to create a default user
in the application as part of the installation. On first login the user has to update their password.
Set keycloak.initUser.enabled to true to enable the user.
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Initial client
The keycloak.initClient is used to create a
default service account
in the application as part of the installation. This enables programmatic access to
the kdb Insights Enterprise API.
Set keycloak.initClient.enabled to true to enable the service account.
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
bool |
|
|
|
|
string |
|
|
|
|
string |
|
|
Reset password service
When enabled, this allows your users to reset their forgotten password via email.
You need to configure SMTP server credentials. With this functionality enabled
users have a Forgot Password? prompt appear on their login screen.
Clicking this takes the user through the keycloak
forgot password flow.
Tip
This only applies to users managed within Keycloak and not those from an upstream identity provider. See the authentication docs for more information on user types.
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Password policy
This defines the password policy that is enforced in the system. A default password policy is enabled but allows you to modify as you require.
For example if you are running in a development environment, you might want to disable the password policy completely. On the other hand, if you are running in a production environment, you might want to enforce a stricter policy.
|
variable |
type |
description |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
bool |
Whether a password policy is enabled |
|
|
|
number |
Password history |
24 |
|
|
number |
Minimum password length |
14 |
|
|
number |
Minimum number of upper case characters |
1 |
|
|
number |
Minimum number of lower case characters |
1 |
|
|
number |
Minimum number of special characters |
1 |
|
|
number |
Minimum number of digits |
1 |
|
|
number |
Time until password expiry in days |
90 |
|
|
string |
HTML text to display the policy on the password update page |
The password policy text is shown on the Update password screen
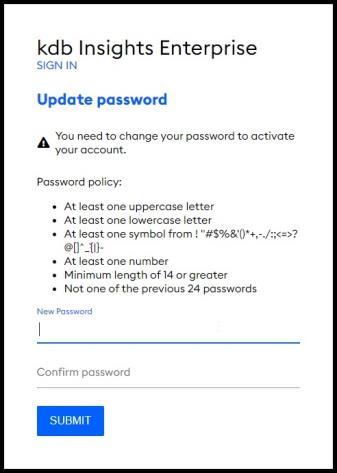
Post deployment, the password policy settings can be adjusted by following the Keycloak password policy documentation.
The password policy text can be adjusted post deployment by following the steps in the advanced docs. This does not automatically update if the settings are changed in Keycloak, so you must ensure it is kept in sync if the settings are changed.
Note
Shared Keycloak instancesWhen using a shared Keycloak instance, the password policy text displayed on the Update password screen is shared across all realms.
This means you must ensure that all realms have the same password policy settings in order for the password policy text to accurately reflect the policy.
If this is not ensured, it can lead to situations where the text on the screen does not accurately reflect the policy being enforced.
Default password policy text
HTML
<p>Password policy:</p>
<ul>
<li>At least one uppercase letter</li>
<li>At least one lowercase letter</li>
<li>At least one symbol</li>
<li>At least one number</li>
<li>Minimum length of 14 or greater</li>
<li>Not one of the previous 24 passwords</li>
</ul>
TLS certificate renewals
The kdb Insights language interfaces use TLS certificates for securing publish and query traffic. These certificates are automatically provisioned and renewed by the application (via cert-manager). The configuration values below determine the duration of the certs and how long before expiry they renew.
YAML
client-controller:
env:
KXI_CERT_RENEW_BEFORE: "15m"
KXI_CERT_DURATION: "1h"
|
variable |
type |
example |
default |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
string |
|
|
|
|
string |
|
|
Tip
Renewal settings
The example values in the table above create certs valid for 1 hour and renewed 15 minutes before they expire.
These values are specified in Parse duration format.
Internal load balancers
kdb Insights Enterprise language interfaces use external load balancers for publishing data into the application. For out of the box security, these are configured as internal by default. This means they are only accessible from within the same virtual network as the Kubernetes cluster itself.
Should you wish to expose your load balancers outside of your virtual network, you can update your values file as below:
YAML
global:
service:
useInternalLBAnnotations: false
Services marked as internal are setup with annotations. These annotations vary across cloud providers. Below shows an example service object with the internal annotations applied:
YAML
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: insights-sg-gateway-tcps
annotations:
networking.gke.io/load-balancer-type: Internal
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-attributes: load_balancing.cross_zone.enabled=true
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-nlb-target-type: instance
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-target-group-attributes: preserve_client_ip.enabled=false
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-type: external
service.beta.kubernetes.io/azure-load-balancer-internal: "true"
Please refer to your Cloud provider documentation for full details on these annotations. Some information is available from the Kubernetes documentation.
Warning
External dependencies
Load balancers can fail to provision in some circumstances. There can be numerous reasons for this,
for example exhausted quotas. You can use kubectl describe on the load balancer service to get more information.
On AWS, the AWS load balancer controller is required to provision internal load balancers. In case of failures, the AWS console can show more information under EC2 → Load Balancers.