Deploy a Kubernetes cluster on ACS
This procedure provides instructions for setting up and configuring a Kubernetes (AKS) cluster on ACS (Azure Cloud Services) using Terraform-based deployment scripts.
The goal is to prepare the infrastructure required to install kdb Insights Enterprise, ensuring that:
-
Core components such as the Virtual Network (VNET), bastion host, security groups, node groups, and associated services are provisioned automatically.
-
Both new VNET creation and integration with existing VNETs are supported.
-
Configuration is managed through environment variables and architectural profiles, offering flexibility for various deployment scenarios.
All scripts are packaged in the kxi-terraform bundle and executed within a pre-configured Docker container to ensure a consistent and repeatable setup across environments.
The configuration and deployment of your Infrastructure to support kdb Insights Enterprise should take approx 20 minutes to complete.
Terraform artifacts
If you have a full commercial license, kdb Insights Enterprise provides default Terraform modules packaged as a TGZ artifact available through the KX Downloads Portal.
You need to download the artifact and extract it as explained in the following sections.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial you need:
-
An Azure Account.
-
An Azure Service Principal.
-
Access to an Authoritative DNS Service (for example, Azure DNS) to create a DNS record for your kdb Insights Enterprise external URL exposed through the clusters Ingress Controller.
-
CA-signed certificate
(cert.pemandcert.keyfiles) for your clusters desired Hostname or a wilcard certifate for your DNS sub-domain, for example, *.foo.kx.com -
Sufficient Quotas to deploy the cluster.
-
A client machine with Azure CLI.
-
A client machine with Docker.
Important
When running the scripts from a bastion host, ensure ports 1174 and 443 are open for outbound access, or enable full outbound access with a 0.0.0.0/0 security group rule.
Note
-
On Linux, additional steps are required to manage Docker as a non-root user.
-
These scripts also support deployment to an existing VNET (Virtual Network) on GCP. If you already have a VPC, you must have access to the associated project to retrieve the necessary network details. Additionally, ensure that your environment meets the prerequisites outlined in the following section before proceeding with deployment to an existing VPC.
Prerequisites for existing VNET
A VNET with the following:
-
One Subnet
-
Subnet Network Security Group must allow HTTP (80) and HTTPS (443) from CIDR's that need access to Insights.
-
A bastion host to be used to deploy the terraform code and Insights.
Billable Azure services
The following Azure services incur charges for this configuration stage (based on the Terraform plan):
- Azure Virtual Machines (Compute) —
- Bastion Linux VM.
- AKS node pool VM instances (Virtual Machine Scale Set).
- Azure Managed Disks — OS disks for the bastion VM and AKS nodes, plus persistent volumes provisioned via the
premium2-diskStorageClass and Rook-Ceph OSD PVCs. - Azure Files — file shares provisioned via the
sharedfilesStorageClass (Standard_ZRS). - Azure Load Balancer (Standard) — provisioned by AKS (outbound type loadBalancer) and by the
ingress-nginxService. - Public IPv4 addresses — static public IP for the bastion host and load balancer frontends.
- Network egress — internet egress via the load balancer and any inter-zone data transfer.
Environment setup
To extract the artifact, execute the following:
Bash
tar xzvf kxi-terraform-*.tgzThis command creates the kxi-terraform directory. The commands below are executed within this directory and thus use relative paths.
To change this directory, execute the following:
Bash
cd kxi-terraformThe deployment process is performed within a Docker container which includes all tools needed by the provided scripts. A Dockerfile is provided in theconfig directory that can be used to build the Docker image. The image name should be kxi-terraform and can be built using the below command:
Bash
docker build -t kxi-terraform:latest ./configService Principal setup
The following Terraform scripts require a Service Principal with appropriate permissions which are defined in the config/kxi-azure-tf-policy.json file. The service principal should already exist.
Note
The below commands should be run by a user with admin privileges.
Update config/kxi-azure-tf-policy.json and replace the following:
-
<role-name>with your desired role name -
<subscription-id>with your Azure Subscription ID
Create role:
Bash
az role definition create --role-definition config/kxi-azure-tf-policy.jsonNote
The role needs to be created only once and then it can be reused.
Assign role to Service Principal:
Bash
az role assignment create --assignee "${CLIENT_ID}" --role "${ROLE_NAME}" --subscription "${SUBSCRIPTION_ID}"where:
-
CLIENT_IDis the Application (client) ID of an existing Service Principal -
ROLE_NAMEis the role name created in the previous step -
SUBSCRIPTION_IDis the Azure Subscription ID
Configuration
The Terraform scripts are driven by environment variables, which configure how the Kubernetes cluster is deployed. These variables are populated by running the configure.sh script as follows.
Bash
./scripts/configure.shSelect Azure and enter your credentials:
Bash
Select Cloud Provider
Choose:
AWS
> Azure
GCPBash
Set Azure Client ID
> a7c7dd92-c0a2-48fd-8ceb-ab134fa41939Bash
Set Azure Client Secret
> ••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••Bash
Set Azure Subscription ID
> 5b07c795-8e5f-4979-aa44-c9bed5b513c5Bash
Set Azure Tenant ID
> c004d551-3955-4f08-9eca-49867395bb69Select the Region to deploy into:
Bash
Select Region
centralindia
centralus
centralusstage
centraluseuap
eastasia
eastasiastage
eastus
eastusstage
eastus2
eastus2stage
eastus2euap
eastusstg
europe
france
francecentral
francesouth
germany
germanynorth
germanywestcentral
india
israel
israelcentral
italy
italynorth
japan
japaneast
japanwest
jioindiacentral
jioindiawest
korea
koreacentral
koreasouth
mexicocentral
newzealand
newzealandnorth
northcentralusSelect the Architecture Profile:
Bash
Select Architecture Profile
Choose:
> HA
Performance
Cost-OptimisedSelect if you are deploying to an existing VNET or want to create one:
Bash
Are you using an existing Virtual Network or wish to create one
Choose:
> New Virtual Network
Existing Virtual Network If you choose Existing Virtual Network, you are asked the following questions; if you select New Virtual Network, skip ahead to the next part.
Bash
Please enter the vnet name of the existing virtual network:
> vnet-abcd
Please enter subnet name:
> vnet-abcd-subnet
Please enter the network security group name which is attached to the bastion host you are deploying from:
> vnet-bastion-sg
Please enter the Azure resource group name where the Virtual Network,Subnet and Network Security Group are created:
> tfscripts-vpc-resource-group If you are using either the Performance or HA profiles, you must enter which storage type to use for rook-ceph.
Bash
Performance uses rook-ceph storage type of managed by default. Press **Enter** to use this or select another storage type:
Choose:
> managed
premium2-diskIf you are using Cost-Optimised, the following is displayed:
Bash
Cost-Optimised uses rook-ceph storage type of managed. If you wish to change this please refer to the docs.Determine how much capacity you require for rook-ceph. To use the default capacity of 100Gi, press Enter.
Bash
Set how much capacity you require for rook-ceph, press Enter to use the default of 100Gi
Note this is the usable storage with replication.
> Enter rook-ceph disk space (default: 100)Enter environment name which acts as an identifier for all resources.
Bash
Set environment name (Up to 8 character, can only contain lowercase letters and numbers)
> insightsNote
When you are deploying to an existing VNET, the following step is not required.
Enter IPs/Subnets in CIDR notation to allow access to the Bastion Host and VPN
Bash
Set Network CIDR that will be allowed VPN access as well as SSH access to the bastion host
For convenience, this is pre-populated with your public IP address (using command: curl -s ipinfo.io/ip).
To specify multiple CIDRs, use a comma-separated list (for example, 192.1.1.1/32,192.1.1.2/32). Do not include quotation marks around the input.
For unrestricted access, set to 0.0.0.0/0. Ensure your network team allows such access.
> 0.0.0.0/0Enter IPs/Subnets in CIDR notation to allow HTTP/HTTPS access to the cluster's ingress.
Bash
Set Network CIDR that will be allowed HTTPS access
For convenience, this is pre-populated with your public IP address (using command: curl -s ipinfo.io/ip).
To specify multiple CIDRs, use a comma-separated list (for example, 192.1.1.1/32,192.1.1.2/32). Do not include quotation marks around the input.
For unrestricted access, set to 0.0.0.0/0. Ensure your network team allows such access.
> 0.0.0.0/0SSL certificate Configuration
Bash
Choose method for managing SSL certificates
----------------------------------------------
Existing Certificates: Requires the SSL certificate to be stored on a Kubernetes Secret on the same namespace where Insights is deployed.
Cert-Manager HTTP Validation: Issues Let's Encrypt Certificates; fully automated but requires unrestricted HTTP access to the cluster.
Choose:
> Existing Certificates
Cert-Manager HTTP Validation Custom tags
The config/default_tags.json file includes the tags that will be applied to all resources. You can add your own tags in this file to customize your environment.
Deployment
To deploy the cluster and apply configuration, execute the following:
Note
A pre-deployment check is performed before proceeding further. If the check fails, the script exits immediately to avoid deployment failures. You must resolve all issues before executing the command again.
This script executes a series of Terraform and custom commands and may take some time to run. If the command fails at any point due to network issues or timeouts, you can execute again until it completes without errors. If the error is related to the Cloud Provider account, for example limits, you must resolve them first before executing the command again.
If any variable in the configuration file needs to be changed, the cluster should be destroyed first and then re-deployed.
For easier searching and filtering, the created resources are named/tagged using the azure-${ENV} prefix. For example, if the ENV is set to demo, all resource names/tags include the azure-demo prefix.
Cluster Access
To access the cluster, execute the following:
This command starts a Shell session on a Docker container, generates a kubeconfig entry, and connects to the VPN. Once the command completes, you can manage the cluster through helm/kubectl.
Note
-
The
kxi-terraformdirectory on the host is mounted on the container on/terraform. Files and directories created while using this container are persisted if they are created under/terraformdirectory even after the container is stopped. -
If other users require access to the cluster, they need to download and extract the artifact, build the Docker container and copy the
kxi-terraform.envfile as well as theterraform/azure/client.ovpnfile (generated during deployment) to their own extracted artifact directory on the same paths. Once these two files are copied, the above script can be used to access the cluster.
The following kubectl commands can be used to retrieve information about the installed components.
-
List Kubernetes Worker Nodes
Bash
Copykubectl get nodes -
List Kubernetes namespaces
Bash
Copykubectl get namespaces -
List cert-manager pods running on cert-manager namespace
Bash
Copykubectl get pods --namespace=cert-manager -
List nginx ingress controller pod running on ingress-nginx namespace
Bash
Copykubectl get pods --namespace=ingress-nginx -
List rook-ceph pods running on rook-ceph namespace
Bash
Copykubectl get pods --namespace=rook-ceph
DNS Configuration
Hostname
When deployingkdb Insights Enterprise you will need to configure a Hostname which you will use to access the application's User Interface. The Hostname should match a record you will create in your domain name system (DNS) service.
DNS Record
When creating your DNS record, the Record name should match the Hostname that you configured when deploying kdb Insights Enterprise (refer to the previous section), and the Value must be the External IP address of the cluster's ingress LoadBalancer as described below. In Azure, the Record type must be set to A.
You can get the cluster's ingress LoadBalancer's External IP by running the following command:
Bash
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-controller
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
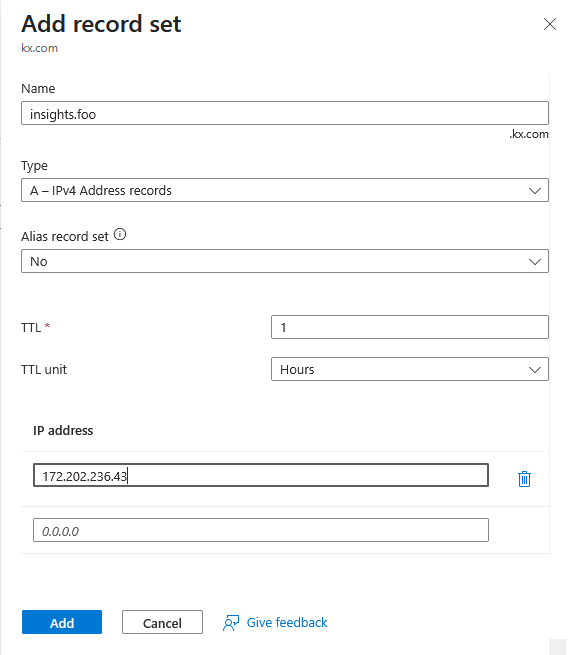
ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.1.253.109 172.202.236.43 80:30941/TCP,443:31437/TCP 110sUsing the output above, create an A record for your hostname which has the value 172.202.236.43.
For example, if your hostname was insights.foo.kx.com, you would create a record in Azure DNS as in the screenshot below.
Ingress Certificate
The hostname used for your kdb Insights Enterprise deployment is required to be covered by a CA-signed certificate.
Note
Self-signed certificates are not supported.
The Terraform scripts support Existing Certificates and Cert-Manager with HTTP Validation.
Existing Certificate
You can generate a certificate for your chosen hostname and pass the cert.pem and cert.key files during the installation of kdb Insights Enterprise.
Cert-Manager with HTTP Validation
Another option for meeting the requirement of a CA-signed coverage is to use cert-manager and Let's Encrypt with HTTP validation. This feature can be enabled by selecting this option during the DNS configuration.
Note
This option introduces a security consideration, because Let's Encrypt must connect to your ingress to verify domain ownership, which necessitates unrestricted access to your ingress LoadBalancer.
Advanced Configuration
There are other automated approaches which are outside the scope of the Terraform scripts. One such approach is to use cert-manager and Let's Encrypt with DNS validation. This option can be configured to work with AWS Route53.
Next Steps
Once you have the DNS configured and have chosen your approach to the Certification of your hostname, you can proceed to the kdb Insights Enterpriseinstallation.
Environment destroy
Before you destroy the environment, make sure you don't have any active shell sessions on the Docker container. You can close the session by executing the following:
Bash
exitTo destroy the cluster, execute the following:
If the command fails at any point due to network issues/timeouts you can execute again until it completes without errors.
Note
-
In some cases, the command may fail due to the VPN being unavailable or Azure resources not cleaned up properly. To resolve this, delete
terraform/azure/client.ovpnfile and execute it again. -
Even after the cluster is destroyed, the disks created dynamically by the application may still be present and incur additional costs. You should review the Azure Disks to verify if the data is still needed.
Uploading and Sharing Cluster Artifacts
To support collaboration, reproducibility, and environment recovery, this Terraform client script provides built-in functionality to upload key configuration artifacts to the cloud backend storage associated with your deployment. These artifacts allow other users or automation systems to connect to the environment securely and consistently.
What Gets Uploaded?
The following files are uploaded to your backend storage under the path ENV which is defined within kxi-terraform.env:
-
version.txt: Contains version metadata for the deployment. -
terraform/aws/client.ovpn: VPN configuration for secure access. -
kxi-terraform.env: The environment file with sensitive credentials removed.
When Are Files Uploaded?
The upload is automatically triggered at the end of the deployment process by:
Bash
./scripts/deploy-cluster.sh
The internal upload_artifacts function performs the upload to the following backend:
- Blob container
(https://${KX_STATE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME}.blob.core.windows.net/${KX_STATE_BUCKET_NAME}/${ENV}/)
These files can then be downloaded by teammates or automation scripts to replicate access and configuration.
You can also run this command manually within the manage-cluster.sh script by running:
Bash
./scripts/terraform.sh upload-artifacts
Cleaning Up Artifacts
To ensure artifacts don’t persist unnecessarily in your backend storage, the system also supports automatic cleanup. These files are deleted at the end of the cluster teardown with the following command:
Bash
./scripts/destroy-cluster.sh
The cleanup is performed by the delete_uploaded_artifacts function and removes the same files from the corresponding ENV location in your backend (stored in kxi-terraform.env).
This keeps your backend clean and prevents the reuse of stale or outdated configuration files.
Advanced configuration
You can further configure your cluster by editing the newly generated kxi-terraform.env file in the current directory. These edits must be made prior to running the deploy-cluster.sh script. The list of variables which can be edited are given below:
|
Environment Variable |
Details |
Default Value |
Possible Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
TF_VAR_enable_metrics |
Enables forwarding of container metrics to Cloud-Native monitoring tools |
false |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_enable_logging |
Enables forwarding of container metrics to Cloud-Native monitoring tools |
false |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_default_node_type |
Node type for default node pool |
Depends on profile |
VM Instance Type |
|
TF_VAR_rook_ceph_pool_node_type |
Node type for Rook-Ceph node pool (when configured) |
Depends on profile |
VM Instance Type |
|
TF_VAR_letsencrypt_account |
If you intend to use cert-manager to issue certificates, then you need to provide a valid email address if you wish to receive notifications related to certificate expiration |
email address |
|
|
TF_VAR_bastion_whitelist_ips |
The list of IPs/Subnets in CIDR notation that are allowed VPN/SSH access to the bastion host. |
N/A |
IP CIDRs |
|
TF_VAR_insights_whitelist_ips |
The list of IPs/Subnets in CIDR notation that are allowed HTTP/HTTPS access to the VPC |
N/A |
IP CIDRs |
|
TF_VAR_letsencrypt_enable_http_validation |
Enables issuing of Let's Encrypt certificates using cert-manager HTTP validation. This is disabled by default to allow only pre-existing certificates. |
false |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_rook_ceph_storage_size |
Size of usable data provided by rook-ceph. |
100Gi |
XXXGi |
|
TF_VAR_enable_cert_manager |
Deploy Cert Manager |
true |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_enable_ingress_nginx |
Deploy Ingress NGINX |
true |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_enable_sharedfiles_storage_class |
Create storage class for shared files |
true |
true / false |
|
TF_VAR_rook_ceph_mds_resources_memory_limit |
The default resource limit is 8Gi. You can override this to change the resource limit of the metadataServer of rook-ceph. Note The MDS Cache uses 50%, so with the default setting, the MDS Cache is set to 4Gi. |
8Gi |
XXGi |
Update whitelisted CIDRs
To modify the whitelisted CIDRs for HTTPS or SSH access, update the following variables in the kxi-terraform.env file:
HCL
# List of IPs or Subnets that will be allowed VPN access as well as SSH access
# to the bastion host for troubleshooting VPN issues.
TF_VAR_bastion_whitelist_ips=["192.168.0.1/32", "192.168.0.2/32"]
# List of IPs or Subnets that will be allowed HTTPS access
TF_VAR_insights_whitelist_ips=["192.168.0.1/32", "192.168.0.2/32"]
Once you have updated these with the correct CIDRs, run the deploy script:
Existing VNET notes
If you're deploying to an existing VNET, ensure that the subnet that is used does not restrict traffic over http (80) and https (443) from the sources you intend to use to access kdb Insights.